the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
Vectors to ore in replacive volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits of the northern Iberian Pyrite Belt: mineral zoning, whole rock geochemistry, and application of portable X-ray fluorescence
Fernando Tornos
Emma Losantos
Juan Manuel Pons
Juan Carlos Videira
In this work we have performed a detailed study of vectors to ore to a representative volcanic-rock-hosted replacive volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposit located in the northern Iberian Pyrite Belt (Spain), the Aguas Teñidas deposit. The investigated vectors include the following: (1) mineralogical zoning, (2) host sequence characterization and mineralized unit identification based on whole rock geochemistry discrimination diagrams, (3) study of the characteristics and behaviour of whole rock geochemical anomalies around the ore (e.g. alteration-related compositional changes, characteristics and extent of geochemical halos of indicative elements such as Cu, Zn, Pb, Sb, Tl, and Ba around the deposit), and (4) application of portable X-ray fluorescence (p-XRF) analysis to the detection of the previous vectors.
In the footwall, a concentric cone-shaped hydrothermal alteration zone bearing the stockwork passes laterally, from core to edge, from quartz (only local) to chlorite–quartz, sericite–chlorite–quartz, and sericite–quartz alteration zones. The hydrothermal alteration is also found in the hanging wall despite being tectonically allochthonous to the orebody: a proximal sericite alteration zone is followed by a more distal albite-rich one. Whole rock major elements show an increase in alteration indexes (e.g. AI, CCPI) towards the mineralization, a general SiO2 enrichment, and FeO enrichment as well as K2O and Na2O depletion towards the centre of the hydrothermal system, with MgO showing a less systematic behaviour. K2O and Na2O leached from the centre of the system are transported and deposited in more external areas. Copper, Pb, and Zn produce proximal anomalies around mineralized areas, with the more mobile Sb, Tl, and Ba generating wider halos. Whereas Sb and Tl halos form around all mineralized areas, Ba anomalies are restricted to areas around the massive sulfide body. Our results show that proposed vectors, or adaptations designed to overcome p-XRF limitations, can be confidently used by analysing unprepared hand specimens, including the external rough curved surface of drill cores.
The data presented in this work are not only applicable to VMS exploration in the Iberian Pyrite Belt, but on a broader scale they will also contribute to improving our general understanding of vectors to ore in replacive-type VMS deposits.
- Article
(28880 KB) - Full-text XML
-
Supplement
(915 KB) - BibTeX
- EndNote
Volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits represent a major source of base (Cu, Pb, Zn), precious (Ag, Au), and other metals (e.g. Co, Sn, In, Cd, Tl, Ga, Se, Sb, Bi) of economic importance (Large et al., 2001a; Franklin et al., 2005). They are distributed in discrete provinces worldwide (e.g. Iberian Pyrite Belt, Spain, Tornos, 2006; southern Urals, Russia, Herrington et al., 2002; Lancones Basin, Peru, Winter et al., 2010; Bathurst Mining Camp, Canada, Goodfellow et al., 2003; Mount Read, Australia, Large et al., 2001a; Kuroko, Japan, Ohmoto, 1996). With the progressive exhaustion of the shallowest and most easily accessible ore deposits, exploration for new resources faces challenges such as exploration at increasing depths, under covered areas (e.g. by unrelated lithological or tectonic units or urbanized areas), or in non-conventional settings, as well as an inevitable need for improved efficiency and lower impact in both environmental and social terms. In this context, the combined study of VMS mineral systems and the development of new exploration strategies and technologies based on geophysical methods and vectors to ore play a vital role.
The use of vectors to ore focuses on the identification and study of lithogeochemical fingerprints produced by the mineralizing hydrothermal system or by subsequent ore remobilizations within and around ore deposits (e.g. Madeisky and Stanley, 1993; Large et al., 2001a; Ames et al., 2016). Vectors to ore have the potential to detect the nearby presence of an ore deposit and to provide information on its likely location or characteristics. They are typically based on the observation of variations in lithology, geochemistry, mineralogy, and mineral chemistry (e.g. Ballantyne, 1981; Large et al., 2001b; Cooke et al., 2017; Mukherjee and Large, 2017; Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a, Hollis et al., 2021) and are characteristic to each deposit type (e.g. trace element mineral chemistry in porphyry–Cu systems: Cooke et al., 2014, 2017; in VMS systems: Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a, b, 2019; in sedimentary exhalative, or SEDEX, systems: Mukherjee and Large, 2017). Additionally, their behaviour may change from district to district, which makes specific characterization of vectors in each district a necessary task for their correct use. Main vectors to ore currently used in VMS systems are shown in Fig. 1.
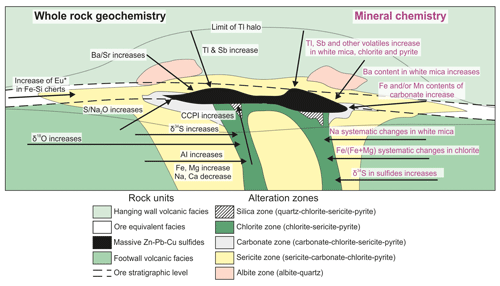
Figure 1Mineralogical and geochemical halos around VMS deposits. Modified from Large et al. (2001a) with data from Lydon (1988), Cathles (1993), Gale and Fedikow (1999), Lenz and Goodfellow (1993), Goodfellow and Peter (1996), Lentz et al. (1997), Brauhart et al. (2001), Large et al. (2001a, b), Gale (2003), Ames et al. (2016), and Soltani Dehnavi et al. (2018a, b, 2019). AI: alteration index (Ishikawa et al., 1976); CCPI: chlorite–carbonate–pyrite index (Large et al., 2001c).
The Iberian Pyrite Belt (IPB) is an outstanding VMS district located in the SW of the Iberian Peninsula (Fig. 2). It is arguably the largest known accumulation of sulfides on the Earth's crust (>1.6 Bt; Tornos, 2006) and represents the main mining area in Spain and one of the main zones of base metal production in Europe. The characterization of vectors to ore in the IPB (e.g. Relvas et al., 1990; Madeisky and Stanley, 1993; Toscano et al., 1994; Costa, 1996; Relvas et al., 2006; Velasco-Acebes et al., 2019) is far from systematic or complete, especially when compared to the work done in other VMS districts (e.g. Australian districts, Large et al., 2001a, and references therein; Bathurst Mining Camp, Canada, Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a, b, 2019). In addition, previous works have mostly focused on the study of the larger shale-hosted exhalative deposits of the southern IPB (e.g. Toscano et al., 1994; Tornos et al., 1998, 2008; Sáez et al., 2011; Velasco-Acebes et al., 2019) or the giant Rio Tinto deposit (e.g. Madeisky and Stanley, 1993; Costa, 1996). However, less attention has been paid to the predominantly volcanic-rock-hosted replacive deposits of the northern IPB (e.g. Relvas, 1990; Sánchez-España et al., 2000; Conde and Tornos, 2020), which, although generally smaller in size compared to southern deposits, typically present higher base metal concentrations (Tornos, 2006). Replacive deposits form by sub-seafloor replacement or favourable lithologies prior to hydrothermal fluid exhalation onto the seafloor (Doyle and Allen, 2003; Tornos et al., 2015); thus, they are expected to produce larger anomalies associated with hydrothermal alteration in the hanging wall area, something that has major implications during exploration.
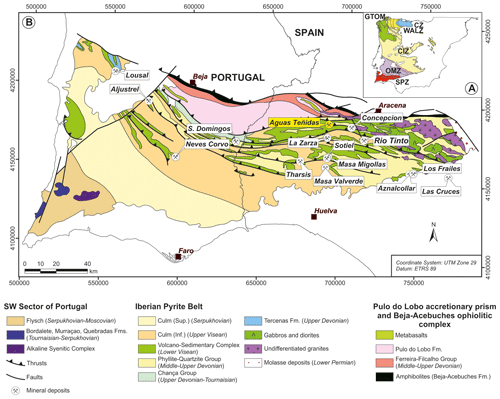
Figure 2Geological map of the South Portuguese Zone and location of the Aguas Teñidas deposit. CZ: Cantabrian Zone; WALZ: West Asturian–Leonese Zone; GTOM: Galicia–Trás-os-Montes Zone: CIZ: Central Iberian Zone; OMZ: Ossa–Morena Zone; SPZ: South Portuguese Zone. Adapted from Martin-Izard et al. (2015), based on IGME (1982).
The aim of this work is to contribute to the characterization of vectors to ore in the IPB by focusing on the study of a representative replacive VMS deposit located in the northern IPB in order to improve mineral exploration and the location of new resources in the area. We have performed a thorough study of the Aguas Teñidas deposit, on which the main vectors to ore currently used in the exploration of VMS systems have been investigated. The massive sulfides and stockwork system of the Aguas Teñidas deposit are hosted in a felsic dome complex with originally homogeneous chemical composition; this has allowed a detailed characterization and study of mineralogical and chemical changes produced on the host rocks by the hydrothermal system during the mineralizing event. Here we present the results of the study and characterization of vectors to ore associated with the mineralogy and whole rock geochemistry of the alteration halo. The latter has included identification of the mineralized unit, study of the characteristics and behaviour of whole rock geochemical anomalies around the ore – with definition of mineralization-related threshold values – and the assessment of the applicability of portable XRF analysis to their detection. New data are compared to data from previous studies on other deposits from this district and from other provinces. Data presented in this work will not only be applicable to exploration in the IPB, but on a broader scale will also contribute to improving our general understanding of vectors to ore in replacive VMS deposits.
2.1 Vectors to ore in VMS systems
Upwelling high-temperature (>350 ∘C) hydrothermal fluids in VMS systems react with the surrounding rocks and sediments, producing chemical and mineralogical changes in the form of alteration halos. These are most developed in the footwall around the feeder zone that underlies the massive sulfides, although they can also form, to a lesser extent, around the deposit and in its hanging wall, especially in sub-seafloor replacive deposits (Large et al., 2001a; Franklin et al., 2005; Hannington, 2014) (Fig. 1). The alteration assemblage is controlled by factors such as rock composition, water rock ratio, temperature, and fluid composition, pH, and redox state (Hannington, 2014). Changes in these controlling factors with depth and distance from the centre of the hydrothermal system typically result in distinct mineralogically and geochemically zoned alteration halos, which are the base for most vectoring tools used in the exploration and characterization of VMS systems (Large et al., 2001a; Gibson et al., 2007) (Fig. 1). The size and morphology of the alteration zones are also controlled by differences in permeability and porosity of the host sequence (Large et al., 2001a; Gibson et al., 2007). However, it is important to bear in mind that mineral assemblages and geochemical zoning patterns observed during exploration are not only the result of the hydrothermal metasomatism associated with the mineralizing event. Instead, they are the result of the combined effects of the initial rock composition and all the processes that have modified it, such as seafloor metasomatism, hydrothermal metasomatism(s), metamorphism, and weathering (Madeisky and Stanley, 1993). These factors may condition and modify patterns formed during mineralization-related hydrothermal alteration and thus need to be considered.
The main vectors to ore used in the exploration and study of VMS systems can be grouped into three main categories: (1) mineralogical zoning, (2) whole rock geochemistry, and (3) mineral chemistry (Fig. 1). In addition, other tools such as identification of mineralization-related lithologies or lithologies indicative of favourable environmental conditions (e.g. anoxic stratigraphic horizons favourable for the formation and preservation of exhalative VMS deposits; Tornos et al., 2015) can also be considered as vectors to ore or pathfinders useful for mineral exploration.
2.2 VMS deposits in the Iberian Pyrite Belt
The IPB belongs to the southernmost domain of the Variscan Belt in the Iberian Peninsula: the South Portuguese Zone (Julivert et al., 1974) (Fig. 2). It holds over 1600 Mt of massive sulfides originally in place and about 250 Mt of stockwork ore in over 90 VMS deposits (Tornos, 2006), including 22 % of the VMS world-class deposits (>32 Mt; Laznicka, 1999; Tornos, 2006). Individual massive sulfide bodies can be up to 170 Mt (La Zarza), and most giant deposits (e.g. Neves Corvo – 200 Mt, Tharsis – 115 Mt, Río Tinto – 500 Mt) include two to six separate bodies located within an area of a few square kilometres (Tornos, 2006).
The IPB VMS deposits were formed from late Famennian to early late Visean times (ca. 360–335 Ma) within a transient transtensional intra-continental pull-apart basin generated on the South Portuguese Zone during the geodynamic evolution leading to the growth of the Variscan orogen in the late Paleozoic (Oliveira, 1990). Crustal thinning and magmatic intrusion triggered the hydrothermal circulation responsible for the massive sulfide mineralizing events (Oliveira, 1990; Oliveira et al., 2004; Mitjavila et al., 1997; Tornos, 2006). A detailed review of the geology and mineralization processes of the IPB can be found in Barriga (1990), Leistel et al. (1998), Carvalho et al. (1999), and Tornos (2006) and is briefly summarized in Sect. S1.1 in the Supplement.
The stratigraphic sequence of the IPB records the pre-, syn-, and post-collisional evolution of the northern continental margin of the South Portuguese Zone terrane. It consists of a 1000–5000 m thick (base not exposed; Tornos, 2006) Devonian to Carboniferous (Oliveira, 1990; Oliveira et al., 2004) sequence which has been divided into three main units (Schermerhorn, 1971). From oldest to youngest, these are the (1) Phyllite–Quartzite Group (PQ), (2) the Volcanic Sedimentary Complex (VSC), which hosts the mineralization, and (3) the Culm Group or Baixo Alentejo Flysch Group. The host VSC consists of a complex bimodal volcanic and shallow intrusive sequence of mantle-derived mafic magmas and crustal felsic magmas, interbedded with mudstone and minor chemical sediments (mainly chert and Fe–Mn-rich sediments) (Munhá, 1983; Mitjavila et al., 1997; Thiéblemont et al., 1998; Tornos, 2006). The VSC in the northern area of the IPB – where the Aguas Teñidas deposit is located (Fig. 2) – is dominated by volcanic materials with minor fine-grained silicic sediments with limited continental influence, whereas the southern area is dominated by shales and siliciclastic sediments with continental influence and minor volcanic and sub-volcanic materials (Quesada, 1996; Sáez et al., 1999; Conde and Tornos, 2020). Two main contrasting styles of VMS mineralization have been described in the IPB which are closely related to the nature of the host stratigraphic sequence: (1) dominantly exhalative shale-hosted deposits (e.g. Sotiel–Migollas, Tharsis, Lousal, Las Cruces, Aznalcóllar–Los Frailes, Masa Valverde) and (2) dominantly replacive felsic–volcanic-rock-hosted deposits (e.g. Aguas Teñidas, La Zarza, Aljustrel, Concepción, La Magdalena) (Relvas et al., 2001, 2002; Tornos et al., 1998, 2008; Tornos, 2006; Tornos and Heinrich, 2008; Velasco-Acebes et al., 2019).
Following deposition of the VSC, compressive tectonism occurred which lasted from the late Visean to late Moscovian (ca. 335–307 Ma) (Oliveira et al., 1979; Silva et al., 1990; Pereira et al., 2008). It disrupted the stratigraphic record of the IPB, forming a thin-skinned foreland fold-and-thrust belt (Ribeiro and Silva, 1983; Silva et al., 1990; Quesada, 1991, 1998) that is S-verging and S-propagating (Spain) as well as SW-verging and SW-propagating (Portugal). The original geometry of the VMS deposits was modified by tectonic dismembering and stacking during this stage (e.g. Relvas et al., 1990; Leistel et al., 1998; Quesada, 1998; Tornos et al., 1998). Associated with compressive tectonics, low-grade regional metamorphism, from prehnite–pumpellyite to low greenschist facies (<350 ∘C), affected rocks in the IPB (Schermerhorn, 1975; Munhá, 1979, 1983, 1990; Sánchez España, 2000). Metal remobilization during the late stages of the Variscan orogeny produced non-economic late vein mineralization within the VSC and Culm Group (Carvalho et al., 1999; McKee, 2003).
2.3 The Aguas Teñidas deposit
Aguas Teñidas is a currently mined polymetallic (Cu–Zn–Pb) massive sulfide deposit located in the northern part of the IPB (Fig. 2b). It was discovered in 1985 during brownfields exploration in the area around the old Aguas Teñidas mine (Hidalgo et al., 1998); further details on the discovery and mining history of this deposit are provided in Sect. S1.2.
2.3.1 Deposit characteristics
The massive sulfide body has an elongated morphology at least 1800 m long, between 150 and 300 m wide, and wedge-shaped perpendicular to elongation with a maximum thickness of 90–100 m by its mostly fault-bounded northern margin (Hidalgo et al., 2000; McKee, 2003) (Figs. 3, 4); it is roughly oriented in an E–W direction and has no surface expression, being located at a depth between 280 m (eastern side) and 650 m (western side), with a plunge of around 20∘ to the W. The massive sulfides have an associated stockwork forming a discordant east–west-trending funnel-shaped (in cross section) zone along the entire deposit (Bobrowicz, 1995; Hidalgo et al., 2000; McKee, 2003) (Figs. 3, 4). Host rocks around the mineralization present pervasive sericitic and chloritic hydrothermal alteration, with a quartz alteration zone in the core of the stockwork (Bobrowicz, 1995) (Fig. 4).
The orebody is intensely deformed, with most of the lithological boundaries being tectonically controlled and the main ore body being crosscut by abundant shear zones (McKee, 2003). Whereas in most areas there is structural continuity between the massive sulfides and the underlying stockwork, the contact between the massive sulfide body and the hanging wall sequence usually consists of a shear zone of unknown displacement (Bobrowicz, 1995; Hidalgo et al., 2000; McKee, 2003) (Fig. 4). This is common in the IPB, where the hanging wall of the massive sulfides is typically over-thrusted above them (Tornos, 2006). The preferential formation of thrusts above massive sulfides has been interpreted as a result of the tectonic inversion of the feeder structures and the rheological contrast between massive sulfides and hydrothermally altered host rocks (Quesada, 1998). The E–W Northern Fault at Aguas Teñidas (Fig. 4) has been interpreted as a syn-sedimentary growth fault which acted as the feeder structure to the hydrothermal system (Bobrowicz, 1995; McKee, 2003) and which was reactivated during the Variscan compressive stage (McKee, 2003).
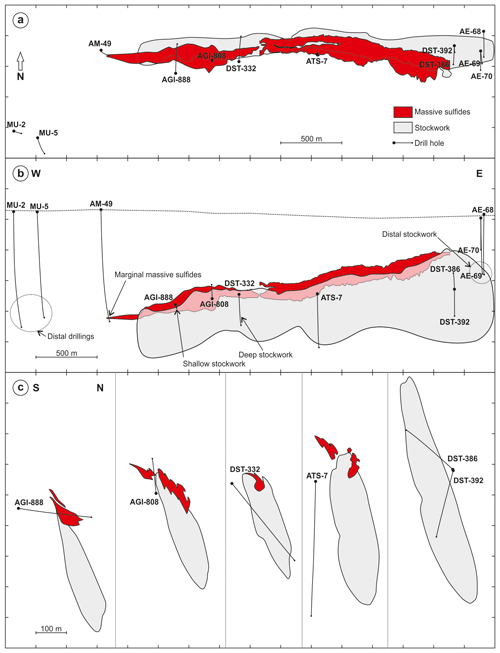
Figure 3Plan view (a), front view (b), and cross sections perpendicular to the deposit elongation (c) of the Aguas Teñidas deposit (massive sulfides and stockwork) and the location of the studied drill holes. The front view (b) is facing N with no vertical exaggeration; the dotted line represents the ground level. Cross sections (c) are facing W with no vertical exaggeration. Data provided by MATSA (Mina de Aguas Teñidas SA).
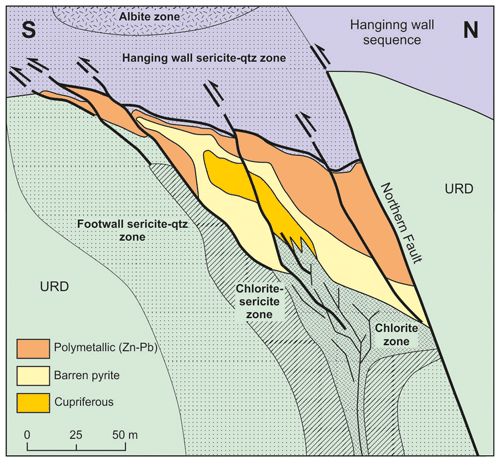
Figure 4Schematic cross section of the Aguas Teñidas deposit based on Sánchez-España et al. (2003). It includes shear zones described by McKee (2003) at the top of the massive sulfides and observed in this study, as well as hanging wall alteration zones described in this study.
At deposit scale the massive sulfide body has a mineral zonation similar to that in other VMS deposits, with a Cu-rich core at the base and Zn–Pb-rich ore towards the top and periphery, although a minor occurrence of Pb, Zn, and Au at the footwall contact deviates from the classical VMS model (Bobrowicz, 1995; McKee, 2003). At metre to decimetre scale it can be highly complex with many repetitions, displacements, and lateral variations (McKee, 2003).
Pyrite, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, and galena account for over 95 % of the massive sulfides, with pyrite generally constituting between 50 % and 80 % of the massive sulfides (Bobrowicz, 1995; Hidalgo et al., 2000). Minor amounts of tetrahedrite–tennantite group minerals, arsenopyrite, stannite, bournonite, and native bismuth are also present, as are trace amounts of fine-grained magnetite (Bobrowicz, 1995; Hidalgo et al., 2000). The gangue is composed of pyrite, quartz, carbonate, and mica.
2.3.2 Host stratigraphic sequence
The stratigraphic sequence hosting the Aguas Teñidas deposit belongs entirely to the VSC. It is dominated by volcanic and sub-volcanic rocks, with minor sedimentary lithologies (predominantly shales) (Bobrowicz, 1995; McKee, 2003; Conde Rivas, 2016; Conde and Tornos, 2020) (Fig. 5). The VSC volcano-stratigraphic sequence in the northern Iberian Pyrite Belt has been subdivided into six tectonostratigraphic units separated by tectonic contacts by Conde Rivas (2016) and Conde and Tornos (2020); their characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The Footwall Felsic Unit and Upper Felsic Unit were interpreted by the authors to belong to a single felsic volcanic complex which was subdivided during tectonic deformation based on facies and geochemical characteristics. In addition, it was suggested that the sequence was tectonically inverted, with the Andesite Unit representing the oldest one (Conde and Tornos, 2020).
The Aguas Teñidas deposit is interpreted to have formed by replacement of the permeable and reactive uppermost autobrecciated and partially devitrified facies of a dacitic dome (Bobrowicz, 1995; Tornos, 2006) of the Footwall Felsic Unit (Conde and Tornos, 2020). The hanging wall of the deposit is characterized by strong vertical and lateral lithological and facies changes, with the main lithologies being red lavas (predominant in the northern part of the deposit), red to purple volcaniclastic rocks, and red or green metapelites (present in the southern part of the deposit) of the Volcano-sedimentary Unit (Hidalgo et al., 2000) (Fig. 5). The host felsic dome was named URD (Unidad Riodacítica; Rhyodacite Unit) by the mining company (Mina de Aguas Teñidas S.A.; MATSA); this local name will be used in this work to differentiate it from the broader Footwall Felsic Unit and Upper Felsic Unit. Similarly, local names of the Hanging Wall Felsic Unit will be also used. The equivalences between unit names used in previous works from Aguas Teñidas (as shown in Fig. 5) and those in Conde and Tornos (2020) are provided in Table 1.
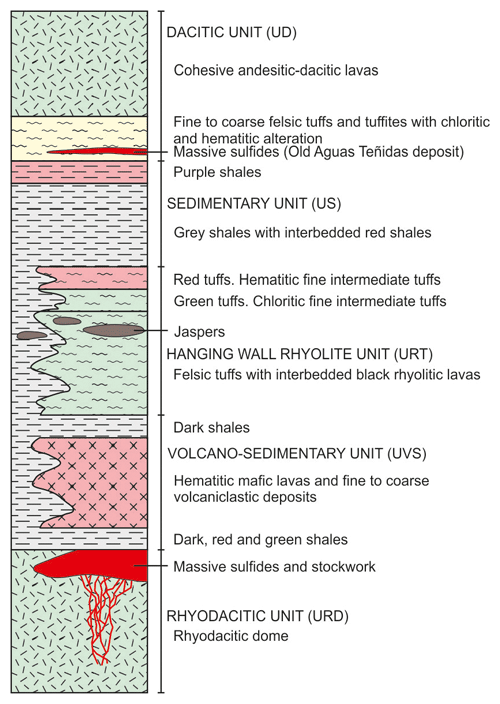
Figure 5Local stratigraphy at the Aguas Teñidas deposit; not to scale. Nomenclature follows original description by MATSA. Modified from MATSA.
Table 1Tectonostratigraphic units in the Lomero Poyatos–Aguas Teñidas zone as defined by Conde and Tornos (2020). Local names used by MATSA and previous works in Aguas Teñidas are given in brackets, with the original acronyms in Spanish for reference.
As in all deposits in the northern IPB, the rocks hosting the Aguas Teñidas deposit underwent three stages of alteration and/or modification: (1) metasomatism and/or alteration of volcanic rocks by interaction with seawater during and soon after emplacement in submarine conditions, which transformed basalts into spilites and felsic rocks into keratophyres and quartz–keratophyres (Munhá and Kerrich, 1980); (2) hydrothermal alteration related to the mineralizing event; and (3) deformation and metamorphism – which in the Aguas Teñidas area only reached the prehnite–pumpellyite facies – and related metal remobilization (Bobrowicz, 1995; Sánchez-España et al., 2000; McKee, 2003).
The investigation of geochemical and mineralogical vectoring tools at the Aguas Teñidas deposit has been performed through the study of samples collected from representative drill cores provided by the MATSA mining company.
3.1 Sampling
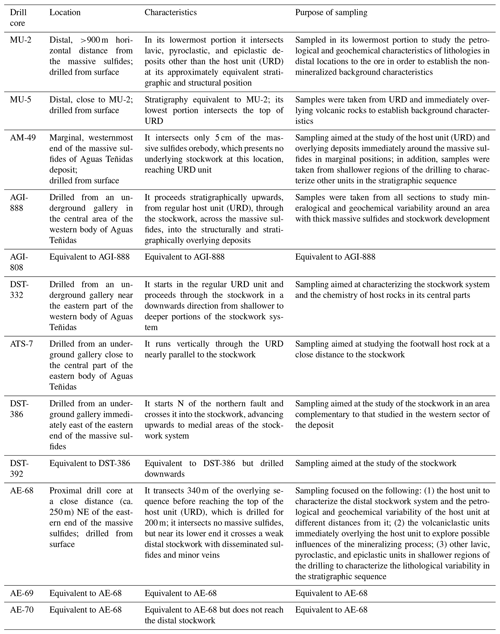
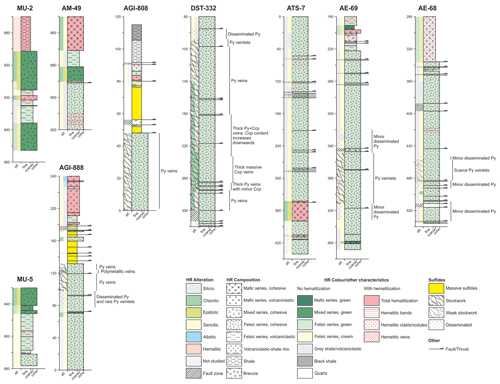
Sampling was aimed at collecting samples from proximal, medial, and distal host rocks to the massive sulfides, as well as from shallow, medial, and deep regions of the stockwork in order to characterize the lithological background and variations with proximity to ore and within the hydrothermal system. A total of 551 samples were collected from 12 drill cores. A list of the studied drill cores and the purpose behind their sampling is provided in Table 2. Their location and relationship to mineralization is shown in Fig. 3. Schematic stratigraphic columns of the portions studied in the main drill cores are presented in Fig. 6. Sample codes consist of the drill core name followed by the depth along the core (in metres) where the sample was collected (e.g. sample MU-2/895.5 was collected at a depth of 895.5 m along core MU-2).
3.2 Analytical methods
A total of 171 representative samples were selected for whole rock geochemical analysis. Sample preparation and analysis of major and trace elements were performed commercially by SGS (Société Générale de Surveillance). Samples were powdered to 85 % passing 75 µm mesh in a Cr-free steel mill. Major elements were analysed by X-ray fluorescence on glass disks prepared by borate fusion. Trace elements were analysed by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) on samples prepared by Na2O2 NaOH fusion followed by dissolution in nitric acid; fusion was performed at low temperatures (ca. 500 ∘C), which reduces the loss of volatile elements. Carbon and S contents were analysed by combustion infrared detection. Precision was better than 1 % (relative standard deviation) for major elements and mostly better than 5 % for trace elements, S, and C. Data on detection limits, precision, and accuracy are provided in Material 2 in the Supplement.
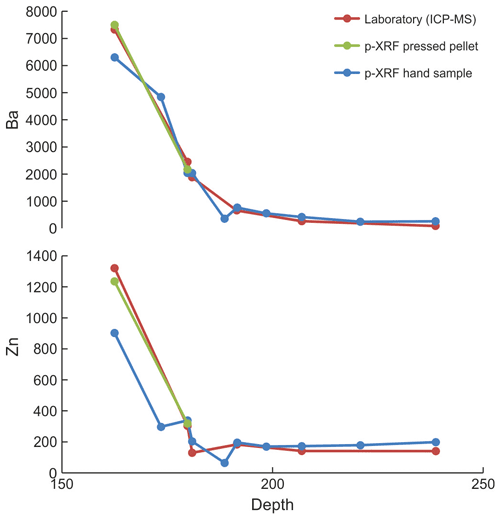
Portable XRF analyses were performed on a selection of samples, including hand specimens (n=15) and pressed pellets (n=15). A Thermo NITON XL3t GOLDD+ was used at the facilities of the Instituto de Geociencias (IGEO) of the Spanish Research Council and Complutense University of Madrid. Prior to sample analysis, an assessment of the performance of our device was made, particularly on the effect of equipment warm-up, measuring time, distance to sample, water content, and number of analyses per sample following the examples and recommendations of previous works (e.g. Ge et al., 2005; Hall et al., 2013, 2014; Bourke and Ross, 2015; McNulty et al., 2020; Laperche and Lemière, 2021); results and discussion of these aspects are presented in Sect. S1.3. Measurements were made using the Cu Zn mining mode with 30 s analysis time per filter (four filters) after an initial 15 min warm-up time at the beginning of each session. A single analysis mode and low counting times (120 s per analysis) were chosen as we consider this to represent realistic and convenient analytical conditions under which exploration work can be carried out (further discussion is available in Sect. S1.3). Equipment calibration was performed by calculating calibration lines from the measurement of pressed powder pellets (15 g of sample pressed at 20 kN for 2 min with no binding materials such as resin or wax) of samples previously analysed for whole rock geochemistry at SGS. These pellets were prepared with the same powder used for whole rock geochemical analysis. A total of 15 samples representative of all lithologies and compositions present around the Aguas Teñidas deposit, plus 2 additional shale samples from the southern IPB, were used. Pellets used for calibration were regularly measured during equipment operation to check for measurement consistency and equipment drift.
Thin sections of 117 representative samples were prepared for petrographic study and mineral chemistry analysis. The petrographic study was performed using a petrographic microscope at the IGEO and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) at the Centro Nacional de Microscopía Electrónica of the Complutense University of Madrid.
4.1 Mineralogical zoning
The mineralogical zoning in alteration halos around VMS deposits has long been used as an empirical vectoring tool worldwide (e.g. Large et al., 2001a, and references therein for Australian deposits). At Aguas Teñidas it was first studied from the observation of the eastern sector of the deposit by Bobrowicz (1995), Hidalgo et al. (2000), McKee et al. (2001), and McKee (2003); they focused on the footwall and described a quartz alteration zone at the core of the hydrothermal system which passes laterally to chlorite, sericite–chlorite, and sericite alteration zones (Fig. 4). The study of new drill cores confirms their observations and allows their extension to the western sector of the deposit. In addition, we identify albitic alteration in the hanging wall for the first time. It is important to bear in mind that the mineral assemblage and textures described here are the result of the original seafloor metasomatism, mineralization-related hydrothermal alteration, and subsequent modification by metamorphism in the prehnite–pumpellyite facies.
Regional alteration
The samples from distal cores (MU-2, MU-5, ca. 900 m from the massive sulfides; Fig. 3) are beyond the influence of hydrothermal alteration related to the Aguas Teñidas deposit, thus providing information on the seafloor metasomatism that dominates the geological background around it. In volcanic and sub-volcanic lithologies the alteration assemblage is largely controlled by the original rock composition (mafic vs. felsic), whereas the degree of alteration is larger in volcaniclastic rocks compared to cohesive lavas. Both mafic (Fig. 7a) and felsic (Fig. 7b) rocks show complete feldspar albitization in the less altered rocks, which progresses to incipient sericitization and formation of chlorite patches in the most altered samples. In mafic rocks the alteration assemblage also includes chlorite, epidote, and minor carbonate, whereas in felsic ones it is dominated by muscovite and quartz. Patches of fine-grained chlorite or chlorite + epidote in the groundmass are interpreted as indicative of former mafic phases (e.g. pyroxene), as no mafic minerals are preserved in the studied rocks. Original igneous quartz phenocrysts in felsic rocks (e.g. in URD unit) are typically preserved, although they are variably modified by dissolution and/or overgrowth of epitaxial quartz.
Footwall alteration
In a more proximal setting (e.g. AE-68, AE-69, AE-70; Fig. 3) sericite–quartz alteration dominates within the felsic URD footwall, with the degree of alteration increasing from background lithologies towards the centre of the system. In less altered rocks feldspar phenocryst pseudomorphs – which are evidenced by coarser muscovite crystals – may be preserved within a finer-grained alteration groundmass (Fig. 7c). However, further alteration completely obliterates the original rock texture except for modified remnants of quartz phenocrysts. This alteration assemblage also dominates the distal stockwork (e.g. AE-68, AE-69; Figs. 3, 6), where additional carbonate alteration may also occur (Fig. 7d), and external parts of the proximal stockwork (e.g. AGI-888, AGI-808, DST-332, DST-386). In the central parts of the stockwork system observed in DST-332 and DST-386 (Figs. 3, 6), sericite–quartz alteration transitions to chlorite–quartz alteration (Fig. 7e, f), which is most intense in areas containing chalcopyrite in the sulfide assemblage. In the studied drill cores from this part of the system there are no lithologies other than the URD, and therefore the effect of proximal alteration on them is unknown.
The reconstruction of the geometry of the alteration zones in the footwall of the Aguas Teñidas deposit shows a pervasive, asymmetric, elongated, and concentric cone-shaped hydrothermal alteration zone which bears the stockwork and which passes laterally, from core to edge, from quartz (not observed in this study) to chlorite, sericite–chlorite, and sericite zones (Bobrowicz, 1995; Hidalgo et al., 2000; McKee et al., 2001), all of them with quartz as an alteration phase (Fig. 4). In the upper parts of the chlorite zone, particularly along its northern and southern contacts with the siliceous zone, chlorite–carbonate alteration zones are also found (Bobrowicz, 1995). Siliceous alteration zones at the centre of the system are not continuous along the deposit; this was considered by McKee (2003) to indicate non-uniform supply of hydrothermal fluids along the feeder system, with location(s) of higher intensity. Hydrothermal alteration transitions to seafloor metasomatism characteristics at the margins of the system.
Hanging wall alteration
Even though the hanging wall to the deposit is mostly tectonically emplaced over the ore (Fig. 4), a proximal sericite alteration zone followed by an albite one in more distal positions has been observed in volcaniclastic rocks of core AGI-888 (Fig. 6). The sericite alteration zone consists of a fine-grained assemblage of muscovite, quartz, and minor to rare (<10 vol %) chlorite, and it occurs in rocks of felsic, intermediate, and mafic compositions (samples AGI-888/179.8, AGI-888/180.9, AGI-888/191.5, and AGI-888/206.9). Albite alteration was observed in a sample from a depth of 238.7 m within volcaniclastic rocks of mafic composition (Fig. 7g). Contrary to albite in distal lithologies (e.g. in cores MU-2 and MU-5), which forms by albitization of igneous feldspars, albite in this alteration zone occurs as a fine-grained groundmass also containing muscovite and minor amounts of chlorite (Fig. 7h). The occurrence of sericitic alteration in hanging wall rocks of felsic to mafic composition indicates a stronger control of the hydrothermal fluid and weaker control of the original rock composition (i.e. higher water rock ratios) compared to zones with dominant seafloor alteration.
Hydrothermal alteration in the hanging wall to the Aguas Teñidas deposit is equivalent to that observed in hanging wall alteration zones clearly associated with VMS deposit formation in other districts (e.g. Large et al., 2001a; Franklin et al., 2005). This indicates that this alteration can be associated with the mineralizing process and, thus, that thrusts and shear zones at the top of the massive sulfides were only affected by minor displacements which were insufficient to decouple the orebody and its associated hydrothermally originated hanging wall alteration. The stratigraphic sequence at Aguas Teñidas is rich in faults and shear zones of unknown displacement; most of these faults occur within given lithological units (e.g. the host dome or even the massive sulfides), therefore also indicating minor displacements. Thus, tectonic deformation at Aguas Teñidas is considered likely to have involved the stacking of many minor structures with small displacement producing an overall “shear-like” deformation rather than fewer structures with larger displacements. Similar tectonic configurations have been described elsewhere in the IPB, such as at the Puebla de Guzmán Antiform (Mantero et al., 2011).
In addition to sericitic and albitic alteration, the hanging wall to the Aguas Teñidas deposit shows a pervasive overprinted oxidizing alteration (Hidalgo et al., 2000; Tornos, 2006) (Fig. 6). This alteration controls the colour of the hanging wall unit and is evidenced at microscale by the occurrence of abundant fine-grained Fe oxides (Fig. 7h). According to Tornos (2006) Fe oxides (magnetite and hematite) replaced pyrite in this unit in zones adjacent to or inside the shear band. This author describes rocks within this structure as showing evidence of syn-deformational oxidation (the shale is purple, and fragments and lenses of reddish silicified rocks are common), which is interpreted as suggesting that the oxidized fluids percolated along these structures during the Variscan orogeny and, thus, that at least part of this hanging wall oxidation was tectonically related.
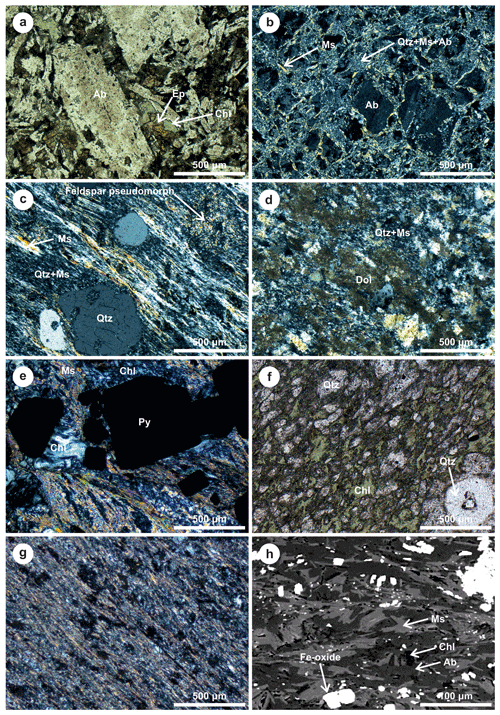
Figure 7Photomicrographs of altered rocks in the host sequence of the Aguas Teñidas deposit. (a) Distal volcanic rock of intermediate composition (sample MU-2/895.5, collected at a depth of 895.5 m along core MU-2) affected by seafloor alteration; plane-polarized light. (b) Distal URD (sample MU-5/875.25) affected by seafloor alteration; cross-polarized light. (c) Hydrothermally altered URD in the sericite alteration zone (sample AE-68/367.6); cross-polarized light. (d) URD in the distal stockwork zone (sample AE-69/384.0), with quartz–sericite and carbonate alteration; cross-polarized light. (e) URD in the medial part of the central stockwork (sample DST-332/139.7), with quartz + sericite + chlorite alteration; cross-polarized light. (f) URD in the central part of the central stockwork (sample DST-332/251.5), with chlorite + quartz alteration – note the preserved quartz phenocrysts; plane-polarized light. (g) Fine-grained mafic volcaniclastic rock in the hanging wall oxidized albitic alteration zone (sample AGI-888/238.7); it consists of a fine-grained muscovite + albite + minor chlorite + iron oxides assemblage; cross-polarized light. (h) Detail of the fine-grained mineral assemblage in sample AGI-888/238.7; backscattered electron scanning electron microscope image. Ab: albite; Chl: chlorite; Dol: dolomite; Ep: epidote; Ms: muscovite; Py: pyrite; Qtz: quartz.
Comparison with VMS deposits in the IPB and other districts
Footwall mineralogical zoning at Aguas Teñidas is equivalent to that found in most volcanic-hosted deposits in the northern Iberian Pyrite Belt, which present an innermost quartz-rich zone (not present in all deposits) enclosed in chlorite-rich and sericite-rich zones (Relvas, 1990; Costa, 1996; Tornos, 2006). An additional ultraperipheral alteration zone with Na-rich mica + quartz ± disseminated pyrite was observed at the Gaviao orebody by Relvas et al. (1990) and Barriga and Relvas (1993) up to 1000 m away from the orebody. In contrast, hydrothermal alteration in the southern IPB is usually dominated by the chloritic type due to the lithological control by the host shale (Tornos et al., 1998; Ruiz et al., 2002). Carbonate alteration is common throughout the IPB (e.g. at Rio Tinto, Tharsis, and La Zarza deposits) and typically occurs in marginal zones of the massive sulfides, at the interface between the sulfides and the underlying stockwork, as independent veins in the stockwork, and as fine-grained disseminations (Williams et al., 1975; Strauss et al., 1981; Tornos et al., 1998). Hanging wall alteration has been poorly characterized in the IPB due to the commonly thrusted character of the hanging walls currently located on top of the massive sulfide bodies (Tornos, 2006); the Aguas Teñidas deposit provides a good example for the understanding of this part of the system.
The mineralogical zoning in the IPB follows that of most typical VMS systems worldwide (Large et al., 2001a; Franklin et al., 2005; Gibson et al., 2007, Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a) (Fig. 1). Hanging wall alteration halos, which are mostly lost in the IPB, are usually minor and dominated by sericite-rich alteration, with local zones of albitic alteration (e.g. Large et al., 2001a), as observed at Aguas Teñidas. Remarkably, in the Bathurst Mining Camp (Canada) an outermost albite–Mg–chlorite alteration zone has been described in both the hanging wall and footwall (Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a, and references therein). The extent of alteration halos tends to correlate with the size of the deposit, with the sericite-rich alteration halo typically extending up to hundreds of metres away from the massive sulfides (e.g. Large et al., 2001a). In the Gaviao orebody of the Aljustrel deposit in the IPB, sericite-rich alteration has been described up to 500 m away from mineralization (Relvas et al., 1990), which is a distance similar to that observed at Rosebery, a replacive-type deposit in the Mount Read Volcanics Belt in Australia (Large et al., 2001b).
Once the mineralogical zoning around a specific hydrothermal system is understood, fast portable mineralogical characterization techniques such as hyperspectral equipment can be used to detect mineralogical changes (in terms of both mineral assemblage and proportions between minerals) in hand specimens and drill cores (e.g. Herrmann et al., 2001; Ross et al., 2019; Hollis et al., 2021). This can be done in nearly real time at minimal expense during ongoing exploration, which allows targeting decisions to be made rapidly.
4.2 Whole rock geochemistry
The new whole rock geochemistry data obtained in this study are provided in Material 2 in the Supplement. These have been used to investigate (1) the composition of the host unit (URD), (2) the behaviour of major elements during hydrothermal alteration, and (3) the trace element geochemical halos around the deposit.
4.2.1 Characterization of the host unit
Identification of lithologies to which mineralization is related (e.g. specific lithological units which host the mineralization), or of lithologies indicative of favourable environmental conditions (e.g. black shales denoting a potentially anoxic seafloor), based on tools such as whole rock geochemistry is traditionally used as a pathfinder to ore deposits in well-characterized host stratigraphic sequences in VMS (e.g. Barret et al., 2005; Schlatter, 2007) and other mineral systems (e.g. SEDEX; Rieger et al., 2021). The chemical characteristics of lithologies in the stratigraphic sequence hosting the Aguas Teñidas deposit have been studied using whole rock geochemistry of immobile major and trace elements. Discrimination diagrams have been elaborated based on ratios of Al, Ti, Zr, and Nb (Fig. 8), which typically present an immobile character under hydrothermal regimes similar to those forming VMS systems (Floyd and Winchester, 1978; MacLean and Kranidiotis, 1987). The use of immobile element ratios in discrimination diagrams has been shown to be effective for unit identification and correlation purposes in other VMS districts (e.g. Barret et al., 2005; Schlatter, 2007) as well as in the study of altered volcanic-dominated stratigraphic sequences in other settings (e.g. Winchester and Floyd, 1977; Gisbert et al., 2017).
Geochemistry of the host stratigraphic sequence
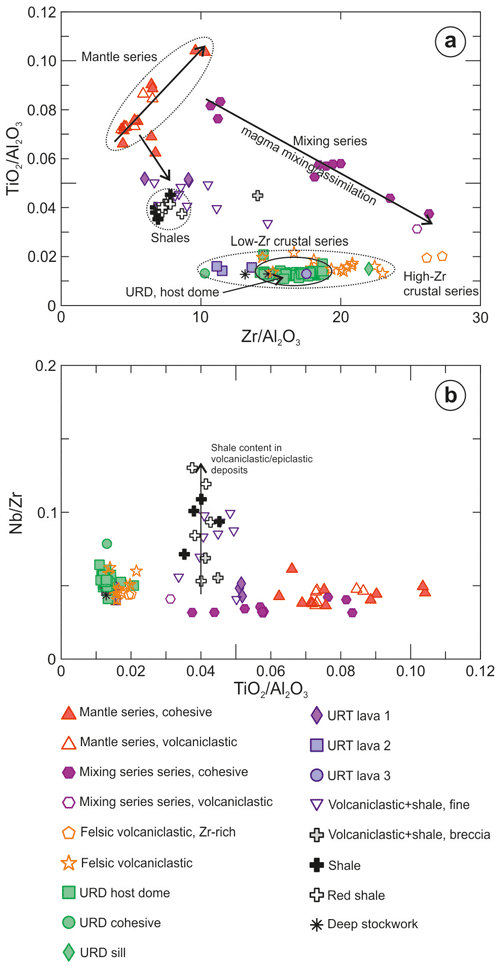
The lithologies studied at Aguas Teñidas include cohesive volcanic and sub-volcanic rocks (as lava domes, lava flows, and sills), breccias of volcanic clasts hosted in shale, coarse volcaniclastic deposits, fine volcaniclastic or epiclastic deposits with variable contents in siliciclastic component, and shales. Samples in Figs. 8 and 9 have been grouped according to their lithology, whole rock geochemistry, and unit – the latter only in the case of cohesive volcanic rocks in the Footwall Felsic Unit and Hanging Wall Felsic Unit, which correspond to the URD and URT units in the mine stratigraphy.
Volcanic rocks are subalkaline in composition, as indicated by low Nb Y (Fig. 9, Pearce, 1996) and Nb Zr (Fig. 8b) ratios. This is consistent with the composition of volcanic rocks in the IPB, where only minor alkaline rocks have been found (Munhá, 1983; Mitjavila et al., 1997; Thieblemont et al., 1997). The two main compositional clusters in Fig. 9 correspond to the mantle-derived basaltic tholeiitic magmas and crust-derived felsic magmas described by Mitjavila et al. (1997); shale compositions are also represented in this diagram as a reference due to the presence of volcaniclastic rocks with variable siliciclastic sediment content.
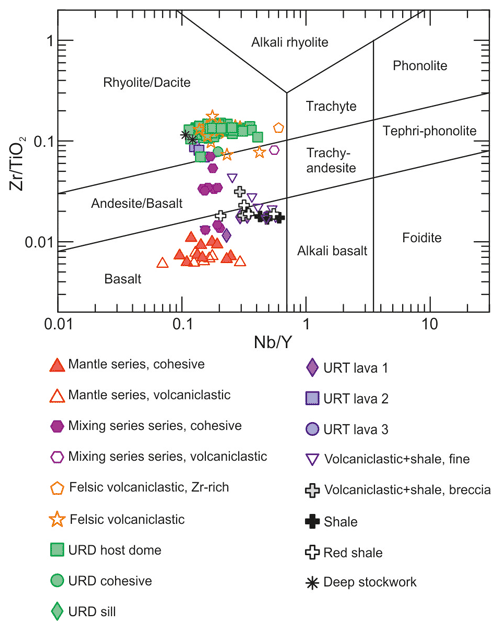
Figure 9Zr TiO2 vs. Nb Y diagram (Pearce, 1996, after Winchester and Floyd, 1977). Ratios are calculated using concentrations in micrograms per gram (µgg−1).
Three main compositional groups are recognized in the TiO2 Al2O3 vs. Zr Al2O3 diagram (Fig. 8a), which is the most useful one for the identification of lithological units and the study of chemical trends in the Aguas Teñidas area: (1) high-TiO2 Al2O3 low-Zr Al2O3 mantle-derived volcanic rocks, (2) low-TiO2 Al2O3 crust-derived volcanic rocks, and (3) shales. In addition, mixed compositions between them exist. High-TiO2 Al2O3 low-Zr Al2O3 volcanic rocks depict a linear trend, which is interpreted as a fractional-crystallization-controlled mantle-derived tholeiitic magma differentiation trend based on the positive correlation between TiO2 Al2O3 and Zr Al2O3 (Fig. 8a), constant Nb Zr (sensitive to mantle partial melting degree), and deviation from mixing trends with crustal material (e.g. shales or compositions equivalent to felsic magmas), which could indicate assimilation or magma mixing. Low-TiO2 Al2O3 volcanic rocks present a wide range of Zr Al2O3, from 10 to over 25 in the analysed samples but reaching over 50 in other rocks from the area (e.g. Conde Rivas, 2016; Conde and Tornos, 2020). This large range may be due to differences in source rock composition (also suggested by differences in Nd isotope compositions in other areas; e.g. Valenzuela et al., 2011; Donaire et al., 2020), variable degrees of partial melting of refractory phases during magma formation (e.g. Rosa et al., 2004, 2006; de Oliveira et al., 2011), and/or magma evolution (e.g. zircon fractionation) prior to emplacement (e.g. Barret et al., 2008). In addition to these two groups, intermediate cohesive lava compositions mark magma mixing trends of mantle-derived magmas with crustal ones from both the high-Zr Al2O3 end (e.g. “mixing series” in Fig. 8a) and low-Zr Al2O3 one (e.g. URT lava 1). Mixing of fine-grained volcaniclastic or epiclastic volcanic products with siliciclastic sediment (shale) is common; these rocks show intermediate Ti Al2O3 contents (Fig. 8a) and higher Nb Zr ratios (Fig. 8b).
Lithological unit identification
The Footwall Felsic Unit, which hosts the mineralization, and the Hanging Wall Felsic Unit are both dominated by crust-derived low-Zr Al2O3 cohesive lavic rocks with minor interbedded lavas and/or intruded sills from the mantle and mixing series (Fig. 8a). Within the Footwall Felsic Unit, the lava dome that hosts the massive sulfides (URD host dome in Fig. 8a) shows a restricted compositional range despite its large dimensions (>2 km long). Below it, drillings have intersected the top of another dome; only one sample (URD cohesive), which presents lower Zr Al2O3 compared to the host dome, has been analysed. A felsic sill currently within the massive sulfides (URD sill) intruded the host unit, likely prior to massive sulfide formation according to facies relationships. This sill presents higher Zr Al2O3 and shows only minor replacement by massive sulfides, which may be due to different texture and/or composition relative to the host lava. From the Hanging Wall Felsic Unit, which was interpreted to be equivalent to the Footwall Felsic Unit by Conde Rivas (2016) and Conde and Tornos (2020), three cohesive felsic lavas were analysed for comparison. URT lava 2 and URT lava 3 are indeed similar in composition to rocks from the Footwall Felsic Unit, within the field of low-Zr Al2O3 rocks. Whereas URT lava 3 falls within the composition of the host dome, URT lava 2 falls outside the compositional field of the host dome between its lower Zr Al2O3 end and the composition of the dome below the host dome (URD cohesive). On the other hand, URT lava 1 shows a significantly different composition, as it is within a possible mixing line between the lower ends of mantle- and crustal-derived magma trends.
Two samples from the chloritic alteration zone at the core of the deep stockwork of the Aguas Teñidas deposit were analysed (deep stockwork in Fig. 8; DST-332, Fig. 3). The original petrographic characteristics of these rocks have been completely erased. However, their whole rock geochemistry indicates that they belong to the Footwall Felsic Unit, likely the host dome (URD, sample DST-332/251.5) or the underlying one (DST-332/275.9) (Fig. 8a). This is consistent with the presence of the host dome around the heavily altered stockwork and shows that the proposed immobile element ratios and discrimination diagrams can also be used for unit and lithology identification even in highly altered zones. Thus, element ratios and discrimination diagrams presented in this work can be used with confidence for the identification of lithological units, including the host one, within the stratigraphic sequence of the Aguas Teñidas deposit.
Comparison with VMS deposits in the IPB
Works dealing with a detailed lithogeochemical characterization of volcanic units hosting and surrounding specific orebodies such as the one presented here for the Aguas Teñidas deposit are scarce in the IPB (e.g. Barret et al., 2008; de Oliveira et al., 2011) as broader studies have typically been performed (e.g. Mitjavila et al., 1997; Sánchez-España et al., 2000; Rosa et al., 2004, 2006; Valenzuela et al., 2011; Conde and Tornos, 2020). However, similar to what has been observed at Aguas Teñidas, available detailed studies usually show the presence of several felsic volcanic units which can be identified based on immobile element ratios like those used here (e.g. Zr Al2O3). For example, at Feitais orebody (Aljustrel), Barret et al. (2008) showed that four rhyolite units in the sequence present different compositional ranges (Zr Al2O3 ca. 10–13, 14–16, 17–20, and 25–26). Similarly, at Lagoa Salgada the host feldspar-and-quartz–phyric rhyodacite hosting the massive sulfides has a Zr Al2O3 ratio of ca. 5.5 to 8, whereas for a barren quartz–phyric rhyodacite this ratio is ca. 8 to 11 (de Oliveira et al., 2011). At the deposit scale this approach can thus be highly useful during deposit exploration and characterization in the heavily tectonized IPB as a vector to locate the mineralized stratigraphic horizon within a previously geochemically characterized sequence. Available detailed studies are insufficient, though, to analyse patterns which could be extrapolated for wider use within the IPB in terms of inferring the barren or fertile character of a given unit according to its whole rock geochemistry. As a first approach, though, it seems that, as seen at Aguas Teñidas as well as at Feitais and Lagoa Salgada, VMS deposits in the IPB are typically related to low-Zr felsic magmas (Rosa et al., 2004, 2006; Valenzuela et al., 2011; Donaire et al., 2020; Conde and Tornos, 2020). In addition, data from Rio Tinto–Nerva and Paymogo Volcano-sedimentary Alignment areas indicate that these magmas also present less radiogenic Nd isotope signatures, which has been interpreted as resulting from shallower partial melting of more evolved crustal rocks (Valenzuela et al., 2011; Donaire et al., 2020). Additional work is needed to confirm these observations.
4.2.2 Vectors to ore based on major elements
Hydrothermal alteration occurs in open-system conditions, under which changes in rock geochemistry occur due to supply or removal of mobile elements (e.g. Si, Fe, Mg, Na, K) (Franklin et al., 2005; Hanington, 2014). Chemical changes can be tracked by observing variations within the system in individual element contents (e.g. gains and losses, usually calculated based on methods such as Pearce element ratios or the isocon method; Pearce, 1968; Grant, 1986; e.g. Madeisky and Stanley, 1993; Barret et al., 2005; Dong et al., 2017), ratios between elements (e.g. Na S; Large et al., 2001a), or commonly used indicator indexes such as (AI; Ishikawa et al., 1976) and the chlorite–carbonate–pyrite index (CCPI; Large et al., 2001c) (e.g. Piercey et al., 2008; Dong et al., 2017). These variations can be used as vectors to ore (e.g. Madeisky and Stanley, 1993; Large et al., 2001b).
Chemical trends observed in the host sequence of the Aguas Teñidas deposit within and around the hydrothermal system are consistent with a major control of hydrothermal fluids on their formation (e.g. Franklin et al., 2005; Large et al., 2001a). This indicates that metamorphism in the prehnite–pumpellyite facies, while it may have produced minor mineralogical or textural modifications, did not induce major changes in whole rock geochemistry, which therefore mainly records the effect of previous alterations (seafloor alteration and mineralization-related hydrothermal alteration; Bobrowicz, 1995; Sánchez-España et al., 2000; McKee, 2003).
Alteration indexes
Samples from distal cores (MU-2 and MU-5) (Fig. 3) were collected beyond the influence area of the hydrothermal system that formed the Aguas Teñidas deposit; therefore, they provide information on the effects of seafloor alteration on rock composition. In mafic rocks from the mantle series, feldspars (presumably plagioclase in origin) are typically completely albitized and partially replaced by chlorite or sericite. Mafic minerals are completely replaced by chlorite and epidote, and the groundmass consists of an assemblage dominated by fine-grained chlorite, epidote, and minor carbonate. Whole rock geochemical changes associated with this alteration are expected to produce minor shifts in the position of these rocks within the alteration box plot (Large et al., 2001c) (Fig. 10); indeed, volcanic rocks of mafic and intermediate composition occur in this diagram within the basalt and andesite field of Large et al. (2001c). In felsic rocks of crustal origin, seafloor alteration is dominated by albitization and variable sericitization of feldspars and groundmass, as well as chloritization of the much scarcer mafic phases. The overall chemical effect is expected to produce a variable shift towards the albite, sericite, and chlorite poles of the alteration box plot (Fig. 10).
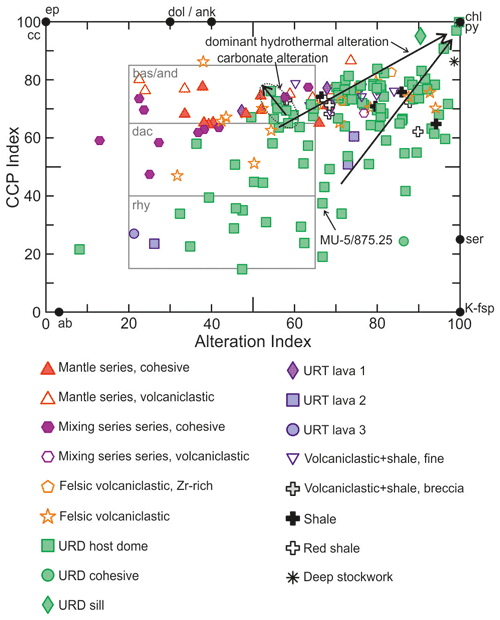
Figure 10Alteration box plot (Large et al., 2001c); the chlorite–carbonate–pyrite index (CCPI) is defined as 100(FeO + MgO) (FeO + MgO + K2O + Na2O), and the alteration index (AI) of Ishikawa et al. (1976) is defined as 100(MgO + K2O) (MgO + K2O + CaO + Na2O). The fields of rhyolitic (rhy), dacitic (dac), and basaltic and andesitic (bas/and) least altered volcanic rocks as described by Large et al. (2001c) based on data from the Rosebery, Que River, and Hellyer areas of the Mount Read Volcanics are depicted. ab: albite; ank: ankerite; chl: chlorite; dol: dolomite; ep: epidote; K-fsp: K-feldspar: py: pyrite; ser: sericite. Samples with carbonate alteration originate in the distal stockwork in cores AE-68 and AE-69.
Hydrothermal alteration adds to the previous modifications induced by seafloor metasomatism. Samples from rocks proximal to or within the hydrothermal system show a compositional convergence towards the chlorite and pyrite vertex (AI = 100, CCPI = 100) of the alteration box plot regardless of the original rock composition (Fig. 10). The observed increase in both alteration indexes is interpreted to be caused by further sericitic and chloritic alteration, as well as by pyrite precipitation, which increase towards the centre of the system. Note that changes in silica content – e.g. resulting from silicification, which is pervasive in most parts of the hydrothermal system in the Aguas Teñidas deposit – are not considered in the plot. The samples closest to the chlorite + pyrite vertex are those from the nearly completely chloritized rocks (with or without accompanying silicification) collected from the chlorite alteration zone or from locally chlorite- or pyrite-rich bands and veins. These correspond to samples from the sill within the massive sulfides (AGI-888/162.5) or the central parts of the stockwork in distal (AE-68), shallow (AGI-888), or deep (DST-332) zones (Fig. 3). Additional local variable carbonate alteration occurs around the Aguas Teñidas deposit. Higher carbonate contents in samples from areas with carbonatic alteration (e.g. distal stockwork in AE-69, URD host dome; marked in Fig. 10) result in a higher CCPI at similar AI.
Downhole CCPI and AI variations are represented in Fig. 11. In core AGI-888, which crosses the massive sulfides, the maximum AI and CCPI values occur by the massive sulfides and decrease away from it, thus representing useful vectors to ore. However, CCPI values in the hanging wall mafic hematitic tuffs are higher than in the immediately underlying felsic tuffs and tuffites, as well as in the footwall URD despite their more distal location relative to mineralization. This is due to the original mafic composition of host rocks (higher initial FeO and MgO contents), which highlights the importance of considering the original rock composition when working with chemical indexes. The lithological control on alteration indexes can also be seen in the rest of the cores. The samples analysed in AE-69 belong mostly to the URD host dome and include the distal stockwork. In the upper portion of the URD index values are constant, becoming more variable around the distal stockwork further down. In this lower area, within this larger variability, AI values slightly increase, while the CCPI decreases slightly; this is due to a decrease in MgO and Na2O coupled with an increase in K2O, which will be discussed later. A higher variability of the alteration indexes around stockwork areas compared to more regular behaviour in more distal host rocks is also seen in ATS-7 and AE-68. This may reflect the more pervasive and homogeneous character of seafloor alteration compared to more focused and permeability-controlled (e.g. related to stockwork structures) hydrothermal alteration.
Element mass changes
Element mass changes were investigated using the isocon method (Grant, 1986), which requires studied rocks to have had a common original chemical composition before alteration (Grant, 1986, 2005). Thus, analysis was restricted to the URD unit as it is the only compositionally homogeneous lithological unit for which least altered to heavily altered compositions were available. After data examination, TiO2, Al2O3, Nb, Ta, Th, and Zr were chosen as reference immobile elements for isocon calculation, and no normalization factors were applied. Sample MU-5/875.25 (marked in the alteration box plot in Fig. 10), which is representative of the least altered URD host dome in the most distal sampled area, was used as the least altered composition. Complete results of this analysis are provided in Material 2 in the Supplement as ΔCi, which represents the absolute difference between the actual concentration of a given element in a rock and the concentration it would have had if it had behaved as immobile. It therefore indicates element mass gains and losses in concentration units (wt % for major elements, ppm for trace elements). ΔCi of MgO, Na2O, and K2O are depicted as examples in downhole diagrams in Fig. 11.
Establishing general trends with distance to ore is difficult given the sampling approach followed in this study. However, the comparison of distal samples (e.g. in core MU-5) with those of the sericite to chlorite alteration zones shows that there is a remarkable generalized mass gain of SiO2 in the area around the Aguas Teñidas deposit, which is accompanied by a smaller gain of MgO and FeO relative to the distal samples, and variable loss or local minor enrichment of Na2O and K2O. In marginal positions to the hydrothermal system (upper URD zones in cores AE-68 and AE-69), FeO, MgO, Na2O, and K2O show a rather constant behaviour in profiles across the host dome above the stockwork zone, indicating a fairly constant effect of seafloor metasomatism throughout the lava dome in this area. K2O depletion and slight Na2O and MgO enrichment in these areas relative to the reference sample likely indicate slightly higher seawater-controlled albitization and sericitization ± chloritization, which may be related to local variability of the regular seafloor metasomatism and/or represent enhanced metasomatism under the influence of the hydrothermal system (this area occurs within the weak sericitic alteration zone).
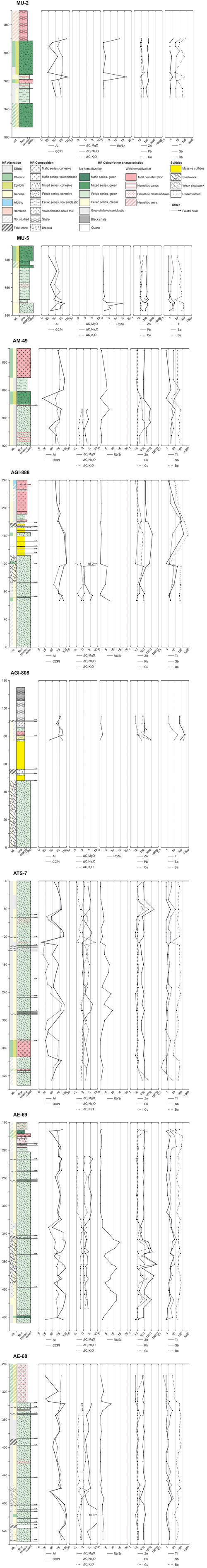
Figure 11Diagrams showing the lithology, alteration assemblages, and whole rock geochemistry of analysed samples. Depth along drill cores is in metres. The AI (alteration index) and CCPI (chlorite–carbonate–pyrite index) are in percent. ΔCi MgO, ΔCi Na2O, and ΔCi K2O are in weight percent (wt %). Trace element contents are in micrograms per gram (µgg−1). Empty circles indicate element contents below the detection limit, which is the marked concentration.
Changes within and by the distal stockwork (Fig. 3, AE-68, AE-69; Fig. 11) reflect the influence of the hydrothermal fluids at the margin of the hydrothermal system. In the most distal AE-68 stockwork zone there is a slight depletion in Na2O associated with MgO enrichment, with no variation in K2O. In the slightly more proximal AE-69, Na2O depletion is coupled with a slight MgO depletion and significant K2O enrichment. In more proximal locations, ATS-7 shows a more chaotic behaviour, likely due to the nearly parallel character of the drill core relative to the margin of the stockwork system. Regarding more internal parts of the stockwork system, rocks in the chlorite-rich alteration zone are markedly enriched in FeO, with less enrichment in MgO (e.g. ΔCi is 28.17 wt % for FeO and 12.39 wt % for MgO in sample DST-332/251.5 in the centre of the deep stockwork). Enrichment in FeO and MgO is coupled with marked Na2O and K2O depletion (e.g. in sample DST-332/251.5 Na2O content is below the detection limit of XRF of 0.01 wt %, and K2O is 0.06 wt %, which represents a ΔCi of −5.22 wt %).
Therefore, there is a general FeO enrichment and alkalis depletion towards the centre of the hydrothermal system, with MgO showing less systematic trends. Regarding alkalies behaviour, whereas even in the most distal samples from the stockwork (AE-68) Na2O is still leached from the host rock, K2O leached from the inner portions of the system seems to be released from the fluid in more proximal locations (e.g. distal stockwork in AE-69); this produces a K2O-rich halo within the external part of stockwork system, with no K2O content modification beyond this distance. An Na2O-richer zone around the hydrothermal system where the Na2O leached from the central parts of the system precipitates is inferred but was not identified in this study. In the footwall it may occur beyond the distal samples in AE-68; in the hanging wall, isocon calculations could not be performed due to the heterogeneous lithologies. It is suggested that an important proportion of the leached Na2O may have been precipitated in the hanging wall and involved in the formation of its sericitic (Na-rich micas are usually found in the hanging wall to VMS deposits; e.g. Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a) and albitic alteration zones.
Remarkably, the highest MgO gains are associated with chlorite-rich veins and/or bands within less chloritic alteration zones (e.g. sericite–quartz alteration zone), such as at a depth of ca. 120 m in AGI-888 (shallow stockwork) or ca. 500 m in AE-68 (distal stockwork). These rocks show marked MgO but negligible FeO enrichment coupled with depletion in Na2O and K2O. We preliminarily interpret this behaviour as due to local circulation of hydrothermal fluids with higher seawater content (cooler and with higher Mg and lower Fe compared to deep hydrothermal fluids).
Pearce element ratios (Pearce, 1968) using Al as an immobile element were also used to study mass changes in the system. Results were similar to those from the isocon method and are therefore not described. Our results are largely consistent with those obtained from a broader but less systematic sampling of the hydrothermally altered halo around the eastern zone of the Aguas Teñidas deposit by Bobrowicz (1995), except for the depletion in SiO2 in the inner system described by the author, which we have not observed. According to Bobrowicz (1995) there are (1) large additions of SiO2 + Fe2O + MgO in the quartz–chlorite central zone of the hydrothermal system, (2) FeO and MgO gain coupled with CaO + Na2O + SiO2 ± K2O depletion in the inner chloritic zone, (3) MgO gain and CaO + Na2O + SiO2 ± K2O loss in the strong sericite–quartz alteration, (4) low SiO2 + Na2O + CaO gain and FeO + MgO + K2O loss in the moderate sericite–quartz alteration, and (5) moderate SiO2 + Na2O gain and general CaO + FeO + MgO + K2O loss in the weak sericite–quartz alteration zone. Bobrowicz (1995) suggested that the observed Si trend resulted from an initial Si-undersaturated character of the upwelling hydrothermal fluids, which produced Si leaching from the centre of the system and subsequent precipitation in the external parts, leading to extensive silicification. The silicified core of the system was interpreted by the author as having formed at a later stage during the hydrothermal event due to a change in fluid conditions.
Comparison with VMS deposits in the IPB and other districts
Chemical trends described in the Aguas Teñidas system are consistent with those reported from other VMS deposits in the IPB (e.g. Relvas, 1990; Madesiky and Stanley, 1993; Costa, 1996; Almodóvar et al., 1998; Sánchez-España et al., 2000; McKee, 2003; Barret et al., 2008; Conde Rivas, 2016). At Rio Tinto, exposure allowed Madesiky and Stanley (1993) to perform a systematic sampling across the hydrothermal system and to study the effects of hydrothermal alteration on three massive (flows and sills) volcanic units (two felsic, one mafic). Analysis based on Pearce element ratios (PERs) showed an overall enrichment in FeO, MgO, and MnO in the feeder zone and up to 1.5 km from its centre, as well as a depletion in CaO, Na2O, and K2O detectable up to 2.5 km from the centre of the feeder system (Madesiky and Stanley, 1993). The alteration index of Ishikawa et al. (1976) presented a positive anomaly similar in extent to the alkali depletion zone. In another study of the Rio Tinto deposit Costa (1996) reported equivalent results, and a similar element behaviour has also been observed at other deposits within the IPB (e.g. Sánchez-España et al., 2000; McKee, 2003). These trends are equivalent to those observed in VMS systems elsewhere (e.g. Large et al., 2001b; Barret et al., 2005), which are dominated by Fe enrichment in the core of the upflow zone, K2O and MgO addition at the margins of the feeding system, and a general loss of CaO and Na2O. They have been related to the formation of Fe and Mg chlorite and muscovite as well as Na- and Ca-bearing plagioclase breakdown, respectively (Hannington, 2014).
In terms of vectors to ore, in the Aljustrel area, Relvas et al. (1990) suggested that a diagram with MgO Al2O3 vs. Na2O (Na2O + K2O) vs. (K2O + BaO) Al2O3 shows the direction of decreasing distance to ore. These ratios illustrate the nearly complete removal of alkalis in the core of the hydrothermal system, followed by a potassic (± Ba) zone (sericite-rich alteration zone), and finally grading into an ultraperipheral external zone where Na is fixed in alteration minerals. Other elemental ratios have also been used as vectoring tools elsewhere, such as S Na2O in the Lens K of the Rosebery deposit (Large et al., 2001b). This ratio varies over 5 orders of magnitude, increasing towards the S-rich, Na-depleted centre of the system. The authors describe it as a good vector within the footwall with sericite- and pyrite-bearing alteration and for up to 50 m into the hanging wall. In weakly developed hanging wall alteration its usefulness is seen to decrease due to the lack of significant sulfide development or albite destruction. According to Large et al. (2001b) S Na2O allows tracking the ore stratigraphic position at locations up to several hundred metres from the ore at this site. The authors note, though, that the S Na2O ratio may also be higher in pyritic shales that are unrelated to mineralization. Behaviour of this ratio at Aguas Teñidas seems to be similar, with an increase in S Na2O towards the ore or centre of the stockwork, but is far from systematic.
4.2.3 Vectors to ore based on trace elements
Vectoring tools based on trace elements usually focus on the detection and study of geochemically anomalous halos of elements related to hydrothermal fluids (e.g. Zn, Pb, Cu, Ba, Sb, and Tl in VMS systems) around and away from deposits (e.g. Large et al., 2001b; Ames et al., 2016; Mukherjee and Large, 2017). Differences exist in the size of these halos depending on the permeability of the medium and the behaviour of trace elements (e.g. solubility, partition coefficients into mineral phases) (Large et al., 2001a; Hannington, 2014). Base metals (e.g. Zn, Pb, Cu) typically produce restricted halos which extend at most some tens of metres to a few hundred metres away from the deposit, whereas the more easily transported volatile elements (e.g. Tl, Sb, Hg) may produce halos which may extend several hundred metres and are therefore amongst the most investigated fluid-mobile elements in VMS systems (Large et al., 2001a; Gibson et al., 2007; Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a). The origin of these halos is still under discussion, as both primary and secondary origins have been proposed (e.g. Germann et al., 2003; Ames et al., 2016).
Threshold values for the Aguas Teñidas area
Geochemical characterization of rocks in proximal (e.g. AGI-808, AGI-888), medial (e.g. AE-68, AE-69), and distal (e.g. MU-2, MU-5) locations relative to the orebody has allowed us to establish the trace element background compositions of rocks in the area and thus to detect changes produced by mineralizing hydrothermal fluids. Generic threshold values have been established above which mineralizing fluids are most likely to have influenced a given rock composition based on (1) our own data from the Aguas Teñidas area and (2) literature data from sedimentary and volcanic rocks of the VSC and PQ groups in Aguas Teñidas and surrounding areas (e.g. Conde and Tornos, 2020) as well as other zones of the Iberian Pyrite Belt (e.g. Sánchez España, 2000). In agreement with existing literature, Zn, Pb, Cu, As, Cd, Sb, and Tl have been found to be the most useful elements. The proposed threshold values for the Aguas Teñidas area are 200 ppm for Zn, 50 ppm for Pb, 150 ppm for Cu, 75 ppm for As (not valid for black shales, which can have higher values unrelated to mineralization), 0.5 ppm for Cd, 15 ppm for Sb, and 2.5 ppm for Tl. However, caution is required in the use of Cd, Sb, and Tl threshold values because only data from this study are available.
Trace element geochemical halos
Downhole plots provide further information on the distribution and behaviour of these elements (Fig. 11). Background values occur (1) in distal cores (MU-2 and MU-5), (2) in upper sections of cores AE-68 and AE-69 away from the distal stockwork, and (3) remarkably also along most of ATS-7, with <20 ppm Cu and Pb, <100 ppm Zn, around 1 ppm Tl, and <5–10 ppm Sb. A minor high in Pb occurs related to red shales in MU-5 immediately on top of the host unit, whose origin is uncertain. In ATS-7, despite its proximity to the stockwork, no anomaly is detected except for a minor local high at a depth of ca. 60 m; this indicates the low permeability of the host dome away from the stockwork and/or a low propagation capacity of the studied elements along this particular lithology. In AE-69 high base metal contents occur within the distal stockwork, whereas Tl and Sb contents are higher by the margins of this system. In the more distal stockwork in AE-68 no base metal anomalies have been detected, whereas slight Tl and Sb ones occur related to the stockwork. AM-49 intersects the margin of the massive sulfides by its western end, cutting only ca. 10 cm of massive sulfides with no associated stockwork. Enriched Pb, Zn, and Tl contents occur in the uppermost part of the URD host dome immediately below the massive sulfides, with concentrations decreasing downwards into the footwall for at least 30 m. Chemical trends in the hanging wall in AM-49 are less clear. Zn content decreases abruptly into the hanging wall, whereas the Tl anomaly seems to show a decreasing trend with a local low in the cohesive lava above the massive sulfides. Cu shows a high in this same lava, likely due to its original mafic composition. AGI-808 and AGI-888 intersect thicker massive sulfides and the underlying external zone of the stockwork in a more central location. Both cores show a geochemical halo of base metals and volatile elements around the massive sulfides, which in AGI-888 peaks for most elements at the sill in the middle of the massive sulfides. Contrary to AM-49, Pb and Zn anomalous concentrations also extend into the hanging wall. Zn presents a larger enrichment and a better-defined geochemical anomaly around the orebody compared to Cu and Pb. In contrast to other cores, in cores AGI-888 and AGI-808 Ba also generates a significant anomaly, with a behaviour that mimics that of Tl. Sb and Tl anomalies extend beyond the limit of those of base metals and Ba, especially in the hanging wall, where positive anomalies occur up to over 50 m above the massive sulfides. It is noteworthy that the chloritic band or vein at a depth of ca. 120 m shows a marked depletion in Tl, Sb, Ba, and Pb relative to the general trends of the respective halos, whereas the trend of Zn content presents no apparent disruption. In core DST-332, sample DST-332/251.5 collected at the centre of the deep stockwork (Figs. 3 and 6) presents 1564 ppm Cu, 65 ppm Zn, Pb below the detection limit (5 ppm), 90 ppm Ba, 2.8 ppm Sb, and Tl below the detection limit (0.5 ppm), indicating marked Cu enrichment, with depletion or no enrichment of all other elements.
Our observations show that Zn, Pb, Cu, Sb, Tl, and Ba geochemical halos with concentrations above those of background rocks occur around the Aguas Teñidas deposit; in addition, they show concentration trends within these halos which allow the use of these elements as vectoring tools. The extent of the halo depends on the element, with Cu producing the most proximal anomalies, followed by Zn and Pb, then Sb, and finally Ba and Tl. For example, in the distal stockwork the Zn and Pb halo reaches AE-69 but not AE-68, where only Tl and Sb anomalies occur. There are differences in the extent and composition of the geochemically anomalous halo along the mineralized system, which are likely related to the intensity and characteristics of the hydrothermal fluid circulation. For example, in marginal locations of the orebody (e.g. AM-49), halos extend to shorter distances compared to more central locations (e.g. AGI-888), especially towards the hanging wall. Moreover, around central parts of the massive sulfide orebody a Ba halo occurs, which is not found in other areas such in marginal areas of the massive sulfides or the stockwork system. Thus, Ba may be a good vector towards the massive sulfides. In the hanging wall of the massive sulfides the concentration of all elements increases towards the massive sulfides. In contrast, a higher complexity exists in the footwall. Whereas Cu contents consistently increase towards the centre of the hydrothermal system, other elements show initial enrichment from background values in distal zones towards the hydrothermal system, which is followed by a depletion towards the centre of the feeder system, with the location of peak concentrations depending on the element. For example, Tl and Sb peak in the most distal stockwork sampled in AE-68, outside the stockwork in AE-69, and in the external shallow stockwork in AGI-888, but they are depleted in the centre of the distal stockwork in AE-69 (less distal than in AE-68) and the deep central stockwork in DST-332. On the other hand, Zn and Pb peak in more internal positions within the stockwork system compared to Tl and Sb and are also depleted in the central zone of the deep stockwork. These observations are consistent with the known mobility of the studied elements in VMS-related hydrothermal systems (Large et al., 2001a; Gibson et al., 2007). Finally, our data also show restrictions on halo formation by host rock permeability, with minor propagation into massive facies (e.g. in AM-49, ATS-7, and AE-69), as seen in other study areas (e.g. Large et al., 2001a; Ames et al., 2016).
Constraints on the relative chronology of geochemical halos
The fact that geochemical halos around the Aguas Teñidas deposit are strongly controlled by the feeder system, with the more mobile elements (e.g. Zn, Pb, Sb, Tl) being depleted in the central parts of the stockwork and enriched by its margins, with concentrations then gradually decreasing towards background contents, strongly suggests that the distribution of these elements was controlled by hydrothermal fluids and, thus, that geochemical halos mainly formed contemporary to or soon after the main orebody formation, either during peak activity or the waning stage. The chlorite-rich vein at ca. 120 m in AGI-888 also provides information on the chronology of geochemical halo formation. This vein strongly contrasts with its host rock in terms of mineralogy and whole rock composition of both major and trace elements. The host rock presents sericite–quartz alteration and follows the regular trend of the base metal and volatile element halos around the massive sulfide. In contrast, this vein shows pervasive chlorite alteration, large Mg enrichment, and depletion of the elements defining the geochemical halos around the massive sulfide orebody except for Zn. Chloritization produced by hydrothermal fluids related to the mineralizing process induces enrichment in Fe supplied by the fluid, as seen in the central deep stockwork in DST-332. In this vein, though, the lack of Fe enrichment indicates a different fluid composition, while exceptional Mg enrichment suggests that it was seawater-dominated. Regarding its relative chronology, negative anomalies in Cu, Pb, Sb, Tl, and Ba compared to the surrounding concentrations in the geochemical halos of these elements suggest that fluid circulation was active at least during and/or after the formation of these geochemical halos. On the other hand, based on the presence of Zn contents consistent with the surrounding geochemical halo we suggest that geochemical halos were already partially established when the chlorite vein system formed and that circulating seawater-dominated fluids subsequently remobilized and leached all indicative elements except for Zn. The different behaviour of Zn may provide information on the circulating fluid properties, whose investigation is beyond the scope of this work. Sub-seafloor shallow mixing of ascending deep hydrothermal fluids with external seawater is regarded as a common process controlling the behaviour and formation of modern and ancient VMS systems, and it is suggested to be driven by seawater convection triggered by the ascent of hot deep hydrothermal fluids (Large et al., 2001a; Franklin et al., 2005; Tornos, 2006; Tornos et al., 2015). We suggest that the aforementioned vein could represent a focused feeder zone of marine water into the hydrothermal system. If this structure is confirmed to be contemporary to the formation of mineralization, this would further support geochemical halos around the ore forming during the active stage of the hydrothermal system and not by subsequent element remobilization, for example during metamorphism. As with hanging wall alteration, the displacement of thrusts and/or shear zones on top of the massive sulfides was insufficient to decouple the orebody and the associated hanging wall geochemical halos.
Search for the seafloor contemporary to the formation of the Aguas Teñidas deposit
Finally, indicative trace elements (e.g. Sb, Tl, Pb, Zn) have been used to investigate the location of the seafloor contemporary to the formation of the Aguas Teñidas orebody within the stratigraphic sequence. Since no potentially syn-mineralization exhalative deposits have been described to date, we searched for geochemically anomalous stratigraphic horizons which could indicate exhalation of hydrothermal fluids at the seafloor. Volcaniclastic materials immediately above the host dome away from the massive sulfides and associated geochemical halo (e.g. in AE-68, AE-69) show no geochemical anomaly which could indicate a preferential circulation of the hydrothermal fluids along these horizons to significant distances or deposition of these materials within a sea-bottom water mass chemically modified by upwelling hydrothermal fluids. The sampling above this immediate hanging wall is not yet detailed enough to locate the potential seafloor, and thus more work is still needed to solve this question.
Comparison with VMS deposits the IPB and other districts
Detailed descriptions of indicator trace elements such as the one presented here are lacking in other deposits of the IPB. However, more general trace element behaviour trends have been studied at other deposits such as Rio Tinto (Piantone et al., 1993, 1994; Costa, 1996), Aljustrel (Barriga, 1983; Relvas, 1991), and Masa Valverde (Toscano et al., 1993). Similar to the Aguas Teñidas deposit, high Tl, Se, Sb, and Hg, as well as relatively high Zn and As contents have been described in halos proximal (up to 500 m) to the mineralization (e.g. Piantone et al., 1993). A strong correlation between Tl and Ba was also observed at Rio Tinto by Costa (1996); these elements are enriched in the sericite alteration zone together with Se and Sb, forming a proximal geochemical anomaly (up to 500 m) relative to the centre of the hydrothermal system (Costa, 1996). Ba enrichment in the sericitic alteration zone also occurs at Aljustrel (Barriga, 1983; Relvas, 1991; Barret et al., 2008) and Masa Valverde (Toscano et al., 1993). At the Feitais orebody in the Aljustrel deposit, the Ba enrichment halo has dimensions of up to tens of metres above and laterally from the orebody, similar to those observed at Aguas Teñidas (Barret et al., 2008).
Geochemical halos of volatile elements (e.g. Tl, Sb, Hg) are a commonly used vectoring tool in other VMS districts (e.g. Mount Read Volcanics, Australia, Large et al., 2001b; Flin Flon Mining Camp, Canada, Ames et al., 2016). The comparison of several VMS systems in Australia by Large et al. (2001a) revealed that there is a relationship between the Zn Cu content of the deposits and the extent of the volatile element halo; Zn-rich deposits (e.g. Rosebery, Hellyer, Thalanga) present larger Tl and Sb halos, whereas in the Cu–Au-type deposits (e.g. Western Tharsis, Highway-Reward) these are more restricted. Rosebery and Hellyer have halos in which Tl and Sb concentrations higher than 1 ppm can be found up to several hundred metres away from the deposit. In contrast, in Thalanga this halo extends less than 50 m into the hanging wall and footwall (Large et al., 2001a). Although analysed less frequently, Hg has also been used as a vectoring tool, for example in the Noranda district and Bathurst Mining Camp (Canada) (Boldy, 1979; Lentz and Goodfellow, 1993). Mercury behaves similarly to Tl and Sb, producing geochemical halos that are more developed in the hanging wall to the deposits (Gibson et al., 2007).
Geochemical halos in VMS deposits in the IPB fall closer to the characteristics of Zn-rich deposits described by Large et al. (2001a), like the Rosebery deposit (Mount Read Volcanics, Tasmania), which can provide a reference for the geometry and size of original halos in less tectonically deformed areas. In Lens K in the Rosebery deposit the Zn and Pb halo reaches about 400 m along the ore stratigraphic horizon and 20 to 50 m across stratigraphy into the footwall (Large et al., 2001b). Cu, which usually requires higher transport temperatures (generally >280 ∘C; Hannington, 2014), produced a significantly smaller halo. In contrast, Tl defines a halo at least 270 m across stratigraphy around the ore position and, opposite to most vectoring tools, is better developed in the hanging wall than in the footwall. In the hanging wall Tl concentrations are higher than 1 ppm for over 200 m; in the footwall the Tl halo extends at least 70 m below the ore lens. At Rosebery Sb varies less systematically than Tl and is therefore recommended to be used in combination with the latter by Large et al. (2001b). The lateral extent of Tl and Sb halos along the ore stratigraphic horizon is over 500 m, beyond the limits of sampling (Large et al., 2001b).
In addition to single elements, trace element ratios have also been used as vectoring tools. For example, in the Lens K of the Rosebery deposit Large et al. (2001b) use the Ba Sr ratio. This ratio increases towards the ore as a result of Ba substitution for K in white mica and Sr depletion due to albite destruction. The authors detect a broad halo of higher Ba Sr that extends up to 80 m into the hanging wall sequence. They consider this ratio to be superior to most other indexes (but not Tl) in defining halos in the hanging wall directly above the ore and for some distance lateral to the ore, but to become a less distinct vector at distal positions from the ore.
4.3 Portable XRF
The vectoring tools based on whole rock geochemistry described in previous sections traditionally rely on conventional laboratory-based XRF and ICP analysis. These techniques provide superior accuracy and precision, as well as lower detection limits. However, they are coupled with high costs – related to both sample preparation and analysis – which usually result in low spatial resolution in systematic studies related to exploration, a long time lapse between sample collection and analytical results, and a destructive character of sample preparation. These aspects reduce the efficiency of these methods for obtaining whole rock geochemistry data during active exploration. Thus, efforts have been devoted to implementing the use of portable XRF as a fast, cost-effective first-stage tool in lithogeochemical exploration in VMS and other mineral systems (e.g. VMS systems, Ross et al., 2014, 2016; McNulty et al., 2018, 2020; Hollis et al., 2021; komatiite-hosted nickel sulfide deposits, Le Vaillant et al., 2014; Au in greenstone belts, Gazley et al., 2011; laterites, Duée et al., 2019) to analyse varied materials such as rocks, soils, or tills (e.g. Hall et al., 2016). The p-XRF technique can be used to obtain geochemical data faster and/or to fill the gaps between traditional laboratory analyses. Taking into account these considerations, we have tested if the lithogeochemical vectors described in previous sections are detectable and usable through direct analysis of core samples by p-XRF.
Several aspects which may affect the quality of the obtained measurements need to be considered before undertaking an exploration study using p-XRF devices. These include the effect on measurements of equipment warm-up, measuring time, calibration method, distance from detector to sample, water content, and sample heterogeneity. All these factors have been assessed in this study and are discussed in detail in Sect. S1.3. Nevertheless, we would like to stress two aspects which are significant for the following discussion. The first one is that factors causing a decrease in the measured intensity (e.g. distance from detector to sample, moisture in or on the sample) tend to have a stronger effect on light elements (Mg, Al, Si) compared to heavier elements (e.g. Ti, Zr), thus producing changes in ratios between elements. For example, our data show that if the distance between the p-XRF device and the sample surface increases to 3 mm (e.g. due to sample irregularity), the measured Al intensity may decrease by up to 45 %, whereas those of Ti and Zr decrease by less than 10 % (Sect. S1.3). The second aspect relates to sample heterogeneity. One of the aims of this study is to evaluate the usefulness of the direct p-XRF analysis of natural rocks for ore exploration. Rocks are naturally heterogeneous at small scale due to factors such as compositional variations along the rock (e.g. changes in sediment composition from layer to layer, presence of veins) or the presence of different minerals (e.g. in coarse-grained igneous rocks). Given the limited area of the spot analysed by p-XRF equipment (typically around 8 mm in diameter), the composition of several spots needs to be averaged to approximate the actual whole rock composition of the studied sample. An assessment of the number of analyses that need to be averaged to obtain a representative whole rock composition is required at each study area, as it depends on lithological characteristics. Our tests have shown that for lithologies like those around the Aguas Teñidas deposit five to seven analyses should be used. In this study we have used 7-point averages in order to work with relative standard deviations in average whole rock compositions usually better than 10 % for all elements (Sect. S1.3) and to minimize the effect of outliers, which may be caused, for example, by the nugget effect in lightly mineralized samples. In porphyritic, hydrothermally altered, tectonically deformed, and metamorphosed rocks with variable occurrence of multiple generations of hydrothermal and metamorphic veins like those investigated in this work, the presence of chemical outliers is common and needs to be considered.
4.3.1 Lithological unit recognition
The p-XRF analysis has been shown to be useful in VMS systems for the discrimination of lithological units (e.g. using Ti Zr, Al Zr, and Zr Y ratios; Ross et al., 2014, 2016). At the Aguas Teñidas deposit the most useful element ratios and diagram for lithological and unit discrimination are Ti Al2O3 vs. Zr Al2O3 (Fig. 8a). Figure 12 compares in this diagram laboratory (XRF + ICP-MS) and p-XRF results (pressed pellet and hand specimen measurements) for five samples representative of the whole compositional range of the host sequence. Pressed powder pellet data occur close to the laboratory data, along trends departing from the axis origin, which are likely due to lower precision in Al measurement compared to Ti and Zr. The same effect can be observed in average hand specimen compositions and on the envelopes containing them. For AM-49/879.75 (average of 21 spots), AE-101.8 (average of 21 spots), and AM-49-108.0 (average of 7 spots), hand specimen results show higher TiO2 Al2O3 and Zr Al2O3 compared to laboratory and pressed pellet data. This is likely due to a differential decrease in the signal of Al on one side and Ti and Zr on the other, caused by sample surface roughness and irregularities (Duée et al., 2019; Sect. S1.3). Data from the hand specimen of sample AE-68/101.8 stress the importance of averaging enough spots for the lithogeochemical characterization of heterogeneous rocks (e.g. due to the presence of veins, banding, or coarse grain size), as the effect of chemical outliers is reduced with the number of averaged spots. In sample AE-68/101.8 two sets of 21 analyses were performed, one on the external curved rough surface of the drill core and another one on the flat cut surface obtained from sawing the core in two. Average compositions are nearly indistinguishable, thus showing that the analysis of the external part of cores is a valid approach and that flat surfaces are not needed. Results from hand specimen analysis of samples AE-69/77.5 and MU-2/913.95 show the importance of monitoring equipment drift during measuring sessions. Due to an unknown error likely related to sensor heating, during the measurement of these two samples light element concentrations – especially Al and Mg – shifted towards unreasonably high concentrations relative to whole rock values. This resulted in erroneously decreased TiO2 Al2O3 and Zr Al2O3 ratios for the drill core surface measurement of MU-2/913.95 and for both hand specimen measurements of AE-69/77.5 (cut surface and core surface). Despite deviation of p-XRF results from laboratory data, the precision of the p-XRF analysis under the chosen conditions is enough to identify the lithology and unit of the studied rocks using the discrimination diagram in Fig. 12. Therefore, p-XRF represents a valuable tool during exploration to differentiate lithologies which may be similar to each other upon visual inspection.
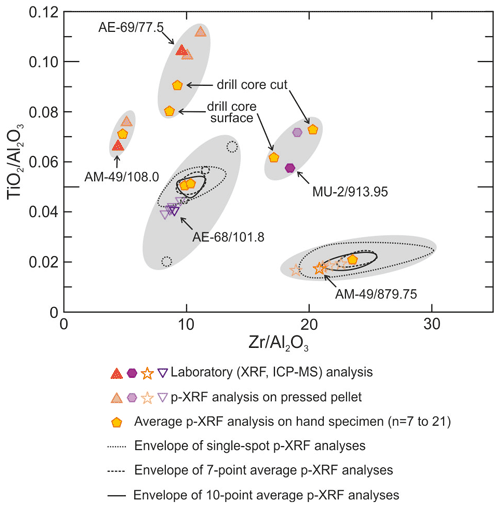
Figure 12TiO2 Al2O3 vs. Zr Al2O3 discrimination diagram comparing whole rock geochemistry data obtained from laboratory (XRF + ICP-MS) and p-XRF analysis of representative samples. For each sample, the data obtained from (1) laboratory analysis (solid symbols), (2) pressed powder pellet p-XRF analysis (faded symbols), and (3) average hand specimen p-XRF analysis (yellow pentagons) are represented. In addition, for samples AM-49/879.75 and AE-68/101.8, the envelopes containing single-spot analyses, 7-point averages, and 10-point averages for hand specimen analyses are also shown to provide a general idea of the effect of multiple spot averaging on analytical precision. Ratios are calculated with TiO2 and Al2O3 contents in weight percent (wt %) and Zr contents in micrograms per gram (µgg−1).
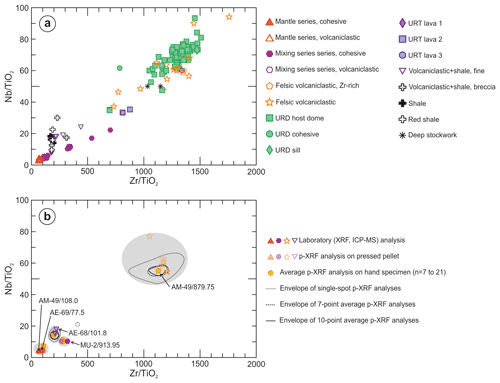
Figure 13Nb TiO2 vs. Zr TiO2 discrimination diagrams showing (a) laboratory whole rock geochemistry data (XRF + ICP-MS) and (b) comparison between laboratory and p-XRF whole rock geochemistry data for representative samples. Ratios are calculated with TiO2 content in weight percent (wt %) and Nb and Zr contents in micrograms per gram (µgg−1).
Figure 12 shows that the highest uncertainties in p-XRF geochemical characterization of both pressed pellets and hand specimens are due to the lower precision in light element determination (particularly Al) relative to heavier ones (e.g. Ti, Zr). Thus, the use of other diagrams avoiding light elements is strongly recommended when working with p-XRF data. The Nb TiO2 vs. Zr TiO2 diagram in Fig. 13 provides an example. Although less efficient at discriminating variations within the mantle series (all data are tightly grouped at low values for both ratios) or mixing series (no discrimination between mixing trends of components with different Zr Al2O3 ratios), this diagram effectively separates (1) mantle, mixing, and crustal series; (2) different compositions within the last class (large compositional range at high values for both ratios); and (3) the presence of a sedimentary component, which produces a departure from the igneous trends towards higher Nb TiO2 values.
4.3.2 Major elements
Na2O and MgO contents, on their own or in ratios (e.g. alteration index), have been shown to be useful indicators of alteration and vectors to ore within the hydrothermal system of VMS deposits in the previous section. However, Na2O cannot be measured by p-XRF devices, and MgO typically presents low precisions (Sect. S1.3). Therefore, alternative ratios using more robust elements have been proposed to track hydrothermal alteration during exploration by p-XRF in VMS systems. For instance, the Rb Sr ratio was suggested to approximate the behaviour of the alteration index by McNulty et al. (2020). At the Myra Falls VMS deposit (Canada), Rb Sr ratios vary from <0.1 for the least altered rocks, 0.1–0.5 for weakly altered rocks, 0.5–1.0 for moderately altered rocks, 1.0–2.0 for strongly altered rocks, to >2.0 for intensely altered rocks (McNulty et al., 2020). Our laboratory data confirm this similarity between the Rb Sr ratio and the alteration index (Fig. 11), which is most evident in AE-69, although differences exist. For example, in core AGI-888, whereas the AI depicts a nearly symmetrical pattern around massive sulfides, higher Rb Sr values only occur within the footwall to the massive sulfides. Therefore, caution is advised in the use of this ratio. Additionally, it is noted that the chlorite band at a depth of around 120 m in AGI-888 shows a low in Rb Sr, as is also the case with other indicators such as Tl, Ba, and Pb, further confirming its singular origin. Figure 14 shows that Rb Sr ratios measured by p-XRF on hand specimens (from both core surface and cut sections) are equivalent to ratios measured on pressed pellets and in the laboratory (ICP-MS). Thus, Rb Sr can be confidently measured using p-XRF devices under the conditions used in this study.
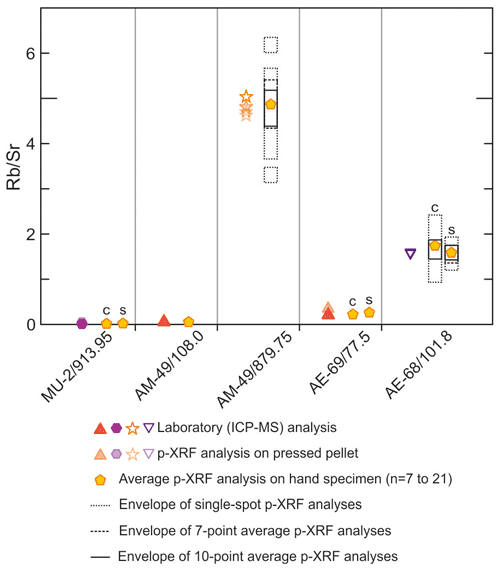
Figure 14Comparison between Rb Sr data obtained from laboratory (ICP-MS) and p-XRF whole rock geochemistry analyses of representative samples. c: cut core section; s: core surface.
4.3.3 Trace elements
To test the usefulness of p-XRF in the analysis of trace elements used in VMS ore exploration, the geochemical halo in the hanging wall to the massive sulfides in core AGI-888 was studied. Figure 15 shows Ba and Zn chemical profiles along the core obtained from the analysis of samples in the laboratory and by p-XRF on hand specimens (10-point average) and pressed pellets (5-point average). More samples were analysed by p-XRF than in the laboratory, showing the usefulness of this tool to fill in the gaps between traditional laboratory data. The Ba p-XRF profile closely matches laboratory data, whereas Zn data show a value lower than expected in sample AGI-888/179.8, which may relate to heterogeneous Zn distribution within the sample. Within the VMS alteration halo Ba is typically hosted in white mica (Large et al., 2001b; Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a), which tends to occur pervasively throughout rocks (Large et al., 2001a; Franklin et al., 2005; Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a); on the other hand, Zn tends to occur (1) in chlorite, to where it partitions preferentially relative to white micas (Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2019), and (2) as sulfides, which may present a more heterogeneous distribution either as disseminate or small veins in lightly mineralized samples, thus presenting a nugget effect (Bourke and Ross, 2015). Since sample AGI-888/179.8 is not mineralized, different Zn concentrations obtained in the p-XRF analysis of the pressed pellet and hand specimen may relate to heterogeneous chlorite distribution at hand specimen scale. This observation stresses the importance of averaging enough analyses per sample. Other useful elements such as Tl and Sb are also typically hosted in white micas, thus presenting a distribution similar to that of Ba (Soltani Dehnavi et al., 2018a), although Tl contents are usually too low for precise p-XRF determination.
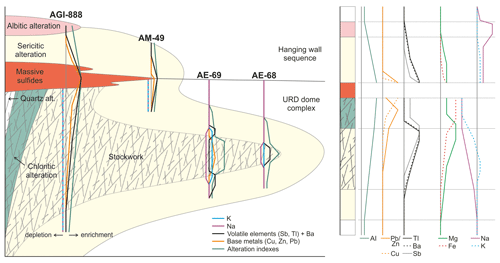
Figure 16Schematic summary of the main observations performed in this study on vectoring tools related to hydrothermal alteration mineral zoning and whole rock geochemistry of major and trace elements. Sodium enrichment in the albite alteration zone is inferred and needs to be confirmed. Not to scale. AI: alteration indexes (AI, CCPI; alt. – alteration).
In this work we have studied and characterized vectors to ore related to mineralogical zoning and whole rock geochemistry in the case study of the Aguas Teñidas replacive volcanic-rock-hosted VMS deposit in the northern IPB.
Alteration halos around the main orebody and associated stockwork show a geometry and distribution equivalent to other VMS deposits in the IPB and other districts (Fig. 16). In the footwall, a concentric cone-shaped hydrothermal alteration zone which bears the stockwork passes laterally, from core to edge, from quartz (only locally) to chlorite, sericite–chlorite, and sericite alteration zones, all of them with quartz as an alteration phase. In the hanging wall, hydrothermal alteration occurs despite its thrusted character; a proximal sericite alteration zone is followed by a more distal albite one. The presence of hydrothermal alteration in the hanging wall indicates that thrusts affecting the hanging wall to the deposit must have had minor displacements.
The lithological units in the host sequence of the Aguas Teñidas deposit have been characterized using whole rock geochemistry. Discrimination diagrams based on immobile element ratios have been presented (TiO2 Al2O3 vs. Zr Al2O3, Nb Zr vs. TiO2 Al2O3) which allow identifying specific units (e.g. the dacitic dome host to the massive sulfides), different magma series (e.g. mantle-derived, crustal-derived, mixing series), and sediment component. The identification of specific lithological units based on whole rock geochemistry represents a powerful exploration tool in a heavily tectonized area such as the IPB.
Major element variations related to hydrothermal alteration useful for vectoring purposes have been studied through the investigation of alteration indexes and mass balance calculations using the isocon method (Fig. 16). The alteration and chlorite–carbonate–pyrite indexes generally increase towards the centre of the system, but caution is required in their use due to the influence of the original rock composition and prior seafloor metasomatism on their final values. Regarding single element variations, only the compositionally homogeneous footwall host unit (URD) could be studied using the isocon method. There is a general FeO enrichment and alkali depletion towards the centre of the hydrothermal system, with MgO showing less systematic trends. Regarding alkali elements, K2O leached from the inner portions of the system was released from the fluid in marginal to distal locations of the stockwork system, producing a K2O-rich band, whereas even in the most distal analysed samples from the stockwork Na2O was still leached from the host rock. An Na2O-richer zone around the hydrothermal system in which the Na2O leached from the central parts precipitates is inferred but has not been identified in this study.
Base metals (Zn, Pb, Cu), volatile elements (Tl, Sb), and Ba have been found to be the most useful trace elements for vectoring purposes at the Aguas Teñidas deposit. Consistent with the known mobility of the studied elements in VMS-related hydrothermal systems, Cu produced the most proximal anomalies, followed by Zn and Pb, then Sb, and finally Ba and Tl (Fig. 16). At the marginal zones of the massive sulfides, base metal halos are mainly restricted to the footwall. In central areas of the massive sulfide orebody, well-developed geochemical halos occur in both the footwall and hanging wall. Remarkably, a significant Ba halo has only been detected around the massive sulfides, indicating the importance of Ba as a vector towards the central part of the hydrothermal system. In the footwall, Cu contents consistently increase towards the centre of the hydrothermal system; in contrast, Zn, Pb, Sb, and Tl show initial enrichment from background contents in distal areas towards the hydrothermal system, which is followed by a depletion towards the centre of the feeder zone, with the location of peak concentrations depending on the element (e.g. margin of the stockwork or immediately outside it for Sb and Tl, within the stockwork for Zn and Pb). In the hanging wall, concentrations in the geochemical halos constantly increase towards the massive sulfides. The characteristics and morphologies of the Cu, Zn, Pb, Sb, Tl, and Ba halos indicate a strong control of the hydrothermal system on their formation, thus showing that they mainly formed contemporary to or soon after the genesis of the main orebody, either during peak activity or the waning stage.
Threshold values have been defined for these trace elements which can be used in the area around the Aguas Teñidas deposit to identify rocks which are likely to have been affected by the mineralizing hydrothermal system. These are 200 ppm for Zn, 50 ppm for Pb, 150 ppm for Cu, 75 ppm for As (not valid for black shales, which can have higher values unrelated to mineralization), 0.5 ppm for Cd, 15 ppm for Sb, and 2.5 ppm for Tl. However, caution is required in the use of Cd, Sb, and Tl threshold values because only data from this study are available.
Trace elements have also provided valuable information related to the genesis and evolution of the deposit. A possible focused feeder zone of seawater into the shallow hydrothermal system has been identified, which was active during and/or soon after formation of the orebody.
Finally, the usefulness of p-XRF devices for the analysis of previously described chemical vectors in realistic exploration conditions has been tested. Our results show that the proposed vectors, or adaptations designed to overcome p-XRF limitations, can be confidently used by analysing unprepared hand specimens, including the external rough curved surface of drill cores.
The results presented in this work contribute to the characterization and understanding of vectors to ore in replacive VMS systems of the IPB, thus improving mineral exploration and the location of new resources in the area. In addition, on a broader scale, the presented data will also contribute to improving our general understanding of vectors to ore in replacive-type VMS deposits elsewhere.
Whole rock geochemistry data used in this work are provided in the Supplement.
The supplement related to this article is available online at: https://doi.org/10.5194/se-12-1931-2021-supplement.
GG was responsible for conceptualization (equal), investigation (lead), and writing the original draft (lead). FT was responsible for conceptualization (equal), funding acquisition (lead), and writing the original draft (supporting). EL was responsible for investigation (supporting) and writing the original draft (supporting). JMP was responsible for investigation (supporting), writing the original draft (supporting), and funding acquisition (supporting). JCV was responsible for investigation (supporting), writing the original draft (supporting), and funding acquisition (supporting).
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Publisher's note: Copernicus Publications remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the special issue “State of the art in mineral exploration”. It is a result of the EGU General Assembly 2020, 3–8 May 2020.
The authors want to thank the following: MATSA for granting access to Aguas Teñidas deposit drill cores, information supplied, and assistance during core investigation and sampling; technicians in the Laboratorio de Petrología y Geoquímica of the Universidad Complutense de Madrid for assistance in sample processing; Jesús Montes for thin section preparation; and Mónica Álvarez and Rafael Fort for granting access to their NITON XL3t 900Analyzer. This research has been conducted within the NEXT (New Exploration Technologies) project and has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement no. 776804.
This research has been supported by Horizon 2020 (NEXT (grant no. 776804)).
We acknowledge support for the publication fee from the CSIC Open Access Publication Support Initiative through its Unit of Information Resources for Research (URICI).
This paper was edited by Liam Bullock and reviewed by two anonymous referees.
Almodóvar, G. R., Sáez, R., Pons, J. M., Maestre, A., Toscano, M., and Pascual, E.: Geology and genesis of the Aznalcóllar massive sulphide deposits, Iberian Pyrite Belt, Spain, Miner. Depos., 33, 111–136, https://doi.org/10.1007/s001260050136, 1998.
Ames, D. E., Galley, A. G., Kjarsgaard, I. M., Tardif, N., and Taylor, B. T.: Hanging-wall vectoring for buried volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits, Paleoproterozoic Flin Flon mining camp, Manitoba, Canada, Econ. Geol., 111, 963–1000, https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.111.4.963, 2016.
Ballantyne, G. H.: Chemical and mineralogical variations in propylitic zones surrounding porphyry copper deposits, PhD, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, 208 pp., 1981.
Barrett, T. J., MacLean, W. H., and Årebäck, H.: The Palaeoproterozoic Kristineberg VMS deposit, Skellefte district, northern Sweden. Part II: chemostratigraphy and alteration, Miner. Depos., 40, 368–395, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-005-0001-2, 2005.
Barrett, T. J., Dawson, G. L., and MacLean, W. H.: Volcanic Stratigraphy, Alteration, and Sea-Floor Setting of the Paleozoic Feitais Massive Sulfide Deposit, Aljustrel, Portugal, Econ. Geol., 103, 215–239, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.103.1.215, 2008.
Barriga, F. J. A. S.: Hydrothermal metamorphism and ore genesis at Aljustrel, Portugal, PhD, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, 386 pp., 1983.
Barriga, F. J. A. S.: Metallogenesis in the Iberian Pyrite Belt, in: Pre-Mesozoic Geology of Iberia, edited by: Dallmeyer, R. D. and Martinez Garcia, E., Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, 369–379, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-83980-1, 1990.
Barriga, F. J. A. S. and Relvas, J. R. M. S.: Hydrothermal alteration as an exploration criterion in the IPB: facts, problems, and future, I Simpósio de Sulfuretos Polimetálicos da Faixa Piritosa Ibérica, Évora, Portugal, 1993,
Bobrowicz, G. L.: Mineralogy, geochemistry and alteration as exploration guides at Aguas Teñidas Este, Pyrite Belt, Spain, Doctor of Philosophy, Faculty of Science and Engineering, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom, 1995.
Boldy, J.: Exploration discoveries, Noranda district, Quebec (Case History of a Mining Camp), in: Geophysics and geochemistry in the search for metallic ores, edited by: Hood, P. J., Economic Geology Report 31, Geological Survey of Canada, 593–603, 1979.
Bourke, A. and Ross, P.-S.: Portable X-ray fluorescence measurements on exploration drill-cores: comparing performance on unprepared cores and powders for “whole-rock” analysis, Geochem-Eplor. Env. A., 16, 147–157, https://doi.org/10.1144/geochem2014-326, 2015.
Brauhart, C. W., Huston, D. L., Groves, D. I., Mikucki, E. J., and Gardoll, S. J.: Geochemical Mass-Transfer Patterns as Indicators of the Architecture of a Complete Volcanic-Hosted Massive Sulfide Hydrothermal Alteration System, Panorama District, Pilbara, Western Australia, Econ. Geol., 96, 1263–1278, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.96.5.1263, 2001.
Carvalho, D., Barriga, F. J. A. S., and Munhá, J.: Bimodal siliciclastic systems – The case of the Iberian Pyrite Belt, in: Volcanic-associated massive sulfide deposits: processes and examples in modern and ancient settings, edited by: Barrie, C. T. and Hannington, M. D., Rev. Econ. Geol., 8, 375–408, 1999.
Cathles, L. M.: Oxygen isotope alteration in the Noranda mining district, Abitibi greenstone belt, Quebec, Econ. Geol., 88, 1483–1511, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.88.6.1483, 1993.
Conde Rivas, C.: Geology and hydrothermal evolution of massive sulphides of the Iberian Pyrite Belt, Spain, Philosophy Doctor, Departamento de Geología, Universidad de Salamanca, Salamanca, Spain, 2016.
Conde, C. and Tornos, F.: Geochemistry and architecture of the host sequence of the massive sulfides in the northern Iberian Pyrite Belt, Ore Geol. Rev., 127, 103042, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103042, 2020.
Cooke, D. R., Baker, M., Hollings, P., Sweet, G., Chang, Z., Danyushevsky, L., Gilbert, S., Zhou, T., White, N. C., Gemmell, J. B., and Inglis, S.: New advances in detecting the distal geochemical footprints of porphyry systems – Epidote mineral chemistry as a tool for vectoring and fertility assessments, in: Building exploration capability for the 21st century, edited by: Kelley, K. D. and Golden, H. C., Special Publication 18, Society of Economic Geologists, Inc., 127–152, 2014.
Cooke, D. R., Agnew, P., Hollings, P., Baker, M., Chang, Z., Wilkinson, J. J., White, N. C., Zhang, L., Thompson, J., Gemmell, J. B., Fox, N., Chen, H., and Wilkinson, C. C.: Porphyry indicator minerals (PIMS) and porphyry vectoring and fertility tools (PVFTS) – Indicators of mineralization styles and recorders of hypogene geochemical dispersion halos, in: Proceedings of Exploration 17: Sixth Decennial International Conference on Mineral Exploration, edited by: Tschirhart, V. and Thomas, M. D., 457–470, Toronto, Canada, 22 to 25 October 2017.
Costa, I. M. S. R.: Efeitos mineralogicos e geochimicos de alteraço mineralizante en rochas vulcanicas felsicas de Rio Tinto (Faixa Piritosa Iberica, Espanha), Master's Degree, Department of Geology, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal, 200 pp., 1996.
de Oliveira, D. P. S., Matos, J. X., Rosa, C. J. P., Rosa, D. R. N., Figueiredo, M. O., Silva, T. P., Guimarães, F., Carvalho, J. R. S., Pinto, Á. M. M., Relvas, J. R. M. S., and Reiser, F. K. M.: The Lagoa Salgada Orebody, Iberian Pyrite Belt, Portugal, Econ. Geol., 106, 1111–1128, https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.106.7.1111, 2011.
Donaire, T., Pascual, E., Sáez, R., Pin, C., Hamilton, M. A., and Toscano, M.: Geochemical and Nd isotopic signature of felsic volcanic rocks as a proxy of volcanic-hosted massive sulphide deposits in the Iberian Pyrite Belt (SW, Spain): The Paymogo Volcano-Sedimentary Alignment, Ore Geol. Rev., 120, 103408, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103408, 2020.
Dong, K., Chen, S., Graham, I., Zhao, J., Fu, P., Xu, Y., Tian, G., Qin, W., and Chen, J.: Geochemical behavior during mineralization and alteration events in the Baiyinchang volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits, Gansu Province, China, Ore Geol. Rev., 91, 559–572, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.09.002, 2017.
Doyle, M. G. and Allen, R. L.: Subsea-floor replacement in volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits, Ore Geol. Rev., 23, 183–222, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1368(03)00035-0, 2003.
Duée, C., Orberger, B., Maubec, N., Laperche, V., Capar, L., Bourguignon, A., Bourrat, X., El Mendili, Y., Chateigner, D., Gascoin, S., Le Guen, M., Rodriguez, C., Trotet, F., Kadar, M., Devaux, K., Ollier, M., Pillière, H., Lefèvre, T., Harang, D., Eijkelkamp, F., Nolte, H., and Koert, P.: Impact of heterogeneities and surface roughness on pXRF, pIR, XRD and Raman analyses: Challenges for on-line, real-time combined mineralogical and chemical analyses on drill cores and implication for “high speed” Ni-laterite exploration, J. Geochem. Explor., 198, 1–17, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.12.010, 2019.
Floyd, P. A. and Winchester, J. A.: Identification and discrimination of altered and metamorphosed volcanic-rocks using immobile elements, Chem. Geol., 21, 291–306, 1978.
Franklin, J. M., Gibson, H. L., Jonasson, I. R., Galley, A. G., Hedenquist, J. W., Thompson, J. F. H., Goldfarb, R. J., and Richards, J. P.: Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits, in: 100th Anniversary Volume, Society of Economic Geologists, 525–560, 2005.
Gale, G. H.: Vectoring volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits using rare earth elements and other pathfinder elements at the Ruttan mine, Manitoba (NTS 63B5), in: Report of Activities 2003, Manitoba Industry, Economic Development and Mines, Manitoba Geological Survey, 54–73, 2003.
Gale, G. H. and Fedikow, M. A. F.: The application of rare earth element analyses in the exploration for volcanogenic massive sulphide type deposits in Manitoba, in: Report of Activities, 1999, Manitoba Industry, Trade and Mines, Geological Services, 9–12, 1999.
Gazley, M. F., Vry, J. K., du Plessis, E., and Handler, M. R.: Application of portable X-ray fluorescence analyses to metabasalt stratigraphy, Plutonic Gold Mine, Western Australia, J. Geochem. Explor., 110, 74–80, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.03.002, 2011.
Ge, L., Lai, W., and Lin, Y.: Influence of and correction for moisture in rocks, soils and sediments on in situ XRF analysis, X-Ray Spectrom., 34, 28–34, https://doi.org/10.1002/xrs.782, 2005.
Germann, K., Lüders, V., Banks, D. A., Simon, K., and Hoefs, J.: Late Hercynian polymetallic vein-type base-metal mineralization in the Iberian Pyrite Belt: fluid-inclusion and stable-isotope geochemistry (S–O–H–Cl), Miner. Depos., 38, 953–967, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-002-0342-z, 2003.
Gibson, H. L., Allen, R. L., Riverin, G., and Lane, T. E.: The VMS model: advances and application to exploration targeting, in: Proceedings of Exploration 07: Fifth Decennial International Conference on Mineral Exploration, edited by: Milkereit, B., 713–730, Toronto, Canada, 9 to 12 September 2007.
Gisbert, G. and Gimeno, D.: Ignimbrite correlation using whole-rock geochemistry: an example from the Sulcis (SW Sardinia, Italy), Geol. Mag., 154, 740–756, https://doi.org/10.1017/s0016756816000327, 2017.
Goodfellow, W. D. and Peter, J. M.: Sulphur isotope composition of the Brunswick No. 12 massive sulphide deposit, Bathurst Mining Camp, New Brunswick: implications for ambient environment, sulphur source, and ore genesis, Can. J. Earth Sci., 33, 231–251, https://doi.org/10.1139/e96-020, 1996.
Goodfellow, W. D., McCutcheon, S. R., and Peter, J. M.: Geologic and Genetic Attributes of Volcanic Sediment-Hosted Massive Sulfide Deposits of the Bathurst Mining Camp, Northern New Brunswick – A Synthesis, in: Massive Sulfide Deposits of the Bathurst Mining Camp, New Brunswick, and Northern Maine, edited by: Goodfellow, W. D., McCutcheon, S. R., and Peter, J. M., Econ. Geol. Monograph, 11, 245–301, https://doi.org/10.5382/Mono.11.13, 2003.
Grant, J. A.: The isocon diagram; a simple solution to Gresens' equation for metasomatic alteration, Econ. Geol., 81, 1976–1982, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.81.8.1976, 1986.
Grant, J. A.: Isocon analysis: A brief review of the method and applications, Phys. Chem. Earth, 30, 997–1004, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2004.11.003, 2005.
Hall, G. E. M., Buchar, A., and Bonham-Carter, G. F.: Quality control assessment of portable XRF analysers: development of standard operating procedures, performance on variable media and recommended uses, CAMIRO Project 10E01, Phase I, 112, 2013.
Hall, G. E. M., Bonham-Carter, G. F., and Buchar, A.: Evaluation of portable X-ray fluorescence (pXRF) in exploration and mining: Phase 1, control reference materials, Geochem-Eplor. Env. A., 14, 99–123, https://doi.org/10.1144/geochem2013-241, 2014.
Hall, G. E. M., McClenaghan, M. B., and Pagé, L.: Application of portable XRF to the direct analysis of till samples from various deposit types in Canada, Geochem-Eplor. Env. A., 16, 62–84, https://doi.org/10.1144/geochem2015-371, 2016.
Hannington, M. D.: 13.18 – Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits, in: Treatise on Geochemistry, Second Edition, edited by: Holland, H. D. and Turekian, K. K., Elsevier, Oxford, 463–488, 2014.
Herrington, R. J., Armstrong, R. N., Zaykov, V. V., Maslennikov, V. V., Tessalina, S. G., Orgeval, J.-J., and Taylor, R. N. A.: Massive Sulfide Deposits in the South Urals: Geological Setting within the Framework of the Uralide Orogen, in: Mountain Building in the Uralides: Pangea to the Present, 155–182, Geophysical Monograph, 132, American Geophysical Union, https://doi.org/10.1029/132GM09, 2002.
Herrmann, W., Blake, M., Doyle, M., Huston, D., Kamprad, J., Merry, N., and Pontual, S.: Short Wavelength Infrared (SWIR) Spectral Analysis of Hydrothermal Alteration Zones Associated with Base Metal Sulfide Deposits at Rosebery and Western Tharsis, Tasmania, and Highway-Reward, Queensland, Econ. Geol., 96, 939–955, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.96.5.939, 2001.
Hidalgo, R., Anderson, I. K., Bobrowicz, G., Ixer, R. A. F., Gaskarth, J. W., and Kettle, R.: The Aguas Teñidas Este deposit, IV Simposio Internacional de Sulfuretos Polimetalicos da Faixa Piritosa Iberica, A15, 1–6, Lisbon, 18–21 January 1998.
Hidalgo, R., Guerrero, V., Pons, J. M., and Anderson, I. K.: The Aguas Teñidas Este mine, Huelva Province, SW Spain, 2000.
Hollis, S. P., Foury, S., Caruso, S., Johnson, S., Barrote, V., and Pumphrey, A.: Lithogeochemical and Hyperspectral Halos to Ag-Zn-Au Mineralization at Nimbus in the Eastern Goldfields Superterrane, Western Australia, Minerals, 11, 254, https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030254, 2021.
IGME: Síntesis Geológica de la Faja Pirítica del SO de España, Instituto Geológico y Minero de España, Madrid, 1982.
Ishikawa, Y., Sawaguchi, T., Iwaya, S., and Horiuchi, M.: Delineation of prospecting targets for Kuroko deposits based on modes of volcanism of underlying dacite and alteration haloes, Mining Geology, 26, 105–117, https://doi.org/10.11456/shigenchishitsu1951.26.105, 1976.
Julivert, M., Fontboté, J. M., Ribeiro, A., and Conde, L.: Mapa tectónico de la Península Ibérica y Baleares, Instituto Geológico y Minero de España, Madrid, 1974.
Laperche, V. and Lemière, B.: Possible Pitfalls in the Analysis of Minerals and Loose Materials by Portable XRF, and How to Overcome Them, Minerals, 11, 33, Geological Survey of Canada, 2021.
Large, R. R., McPhie, J., Gemmell, B., Herrmann, W., and Davidson, G. J.: The spectrum of ore deposit types, volcanic environments, alteration halos, and related exploration vectors in submarine volcanic successions: some examples from Australia, Econ. Geol., 96, 913–938, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.96.5.913, 2001a.
Large, R. R., Allen, R. L., Blake, M. D., and Herrmann, W.: Hydrothermal Alteration and Volatile Element Halos for the Rosebery K Lens Volcanic-Hosted Massive Sulfide Deposit, Western Tasmania, Econ. Geol., 96, 1055–1072, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.96.5.1055, 2001b.
Large, R. R., Gemmell, J. B., Paulick, H., and Huston, D. L.: The alteration box plot: a simple approach to understanding the relationship between alteration mineralogy and lithogeochemistry associated with volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits, Econ. Geol., 96, 957–971, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.96.5.957, 2001c.
Laznicka, P.: Quantitative relationships among giant deposits of metals, Econ. Geol., 94, 455–473, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.94.4.455, 1999.
Le Vaillant, M., Barnes, S. J., Fisher, L., Fiorentini, M. L., and Caruso, S.: Use and calibration of portable X-Ray fluorescence analysers: application to lithogeochemical exploration for komatiite-hosted nickel sulphide deposits, Geochem-Eplor. Env. A., 14, 199–209, https://doi.org/10.1144/geochem2012-166, 2014.
Leistel, J. M., Marcoux, E., Thieblemont, D., Quesada, C., Sanchez, A., Almodovar, G. R., Pascual, E., and Saez, R.: The volcanic-hosted massive sulphide deposits of the Iberian Pyrite Belt – Review and preface to the Thematic Issue, Miner. Depos., 33, 2–30, 1998.
Lentz, D. R. and Goodfellow, W. D.: Geochemistry of the stringer sulfide zone in the discovery hole at the Brunswick No. 12 massive sulfide deposit, Bathurst, New Brunswick, Geological Survey of Canada, Paper 93-1E, 259–269, 1993.
Lydon, J. W.: Ore Deposit Models #14, Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide Deposits Part 2: Genetic Models, Geoscience Canada, 15, 1988.
MacLean, W. H. and Kranidiotis, P.: Immobile elements as monitors of mass transfer in hydrothermal alteration; Phelps Dodge massive sulfide deposit, Matagami, Quebec, Econ. Geol., 82, 951–962, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.82.4.951, 1987.
Madeisky, H. E. and Stanley, C. R.: Lithogeochemical exploration of metasomatic zones associated with volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits using Pearce element ratio analysis, Int. Geol. Rev., 35, 1121–1148, https://doi.org/10.1080/00206819309465580, 1993.
Mantero, E. M., Alonso-Chaves, F. M., García-Navarro, E., and Azor, A.: Tectonic style and structural analysis of the Puebla de Guzmán Antiform (Iberian Pyrite Belt, South Portuguese Zone, SW Spain), Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 349, 203–222, https://doi.org/10.1144/sp349.11, 2011.
Martin-Izard, A., Arias, D., Arias, M., Gumiel, P., Sanderson, D. J., Castañon, C., Lavandeira, A., and Sanchez, J.: A new 3D geological model and interpretation of structural evolution of the world-class Rio Tinto VMS deposit, Iberian Pyrite Belt (Spain), Ore Geol. Rev., 71, 457–476, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.06.006, 2015.
McKee, G. S.: Genesis and deformation of the Aguas Teñidas Este massive sulphide deposit and implications for the formation, structural evolution and exploration of the Iberian Pyrite Belt, Doctor of Philosophy, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2003.
McKee, G. S., Hidalgo, R., Ixer, R. A., Boyce, A., Guerrero, V., and Pons, J. M.: Deposit formation and structural evolution at Aguas Teñidas Este, in: GEODE workshop massive sulfide deposits in the Iberian Pyrite Belt: new advances and comparison with equivalent systems, edited by: Tornos, F., Pascual, E., Sáez, R., and Hidalgo, R., 38–39, Aracena, Spain, 2001.
McNulty, B. A., Fox, N., Berry, R. F., and Gemmell, J. B.: Lithological discrimination of altered volcanic rocks based on systematic portable X-ray fluorescence analysis of drill core at the Myra Falls VHMS deposit, Canada, J. Geochem. Explor., 193, 1–21, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.06.005, 2018.
McNulty, B. A., Fox, N., and Gemmell, J. B.: Assessing hydrothermal alteration intensity in volcanic-hosted massive sulfide systems using portable x-ray fluorescence analysis of drill core: an example from Myra Falls, Canada, Econ. Geol., 115, 443–453, https://doi.org/10.5382/econgeo.4714, 2020.
Mitjavila, J., Martí, J., and Soriano, C.: Magmatic Evolution and Tectonic Setting of the Iberian Pyrite Belt Volcanism, J. Petrol., 38, 727–755, https://doi.org/10.1093/petroj/38.6.727, 1997.
Mukherjee, I. and Large, R.: Application of pyrite trace element chemistry to exploration for SEDEX style Zn-Pb deposits: McArthur Basin, Northern Territory, Australia, Ore Geol. Rev., 81, 1249–1270, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.08.004, 2017.
Munhá, J.: Blue amphiboles, metamorphic regime and plate tectonic modelling in the Iberian Pyrite Belt, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 69, 279–289, https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00372330, 1979.
Munhá, J.: Hercynian magmatism in the Iberian Pyrite Belt, Memórias dos Serviços Geológicos de Portugal, 29, 39–81, 1983.
Munhá, J. and Kerrich, R.: Sea water basalt interaction in spilites from the Iberian Pyrite Belt, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 73, 191–200, https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00371394, 1980.
Munha, J.: Metamorphic Evolution of the South Portuguese/Pulo Do Lobo Zone, in: Pre-Mesozoic Geology of Iberia, edited by: Dallmeyer, R. D. and Garcia, E. M., Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 363–368, 1990.
Ohmoto, H.: Formation of volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits: The Kuroko perspective, Ore Geol. Rev., 10, 135–177, https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-1368(95)00021-6, 1996.
Oliveira, J. T.: South Portuguese Zone: introduction. Stratigraphy and synsedimentary tectonism, in: PreMesozoic Geology of Iberia, edited by: Dallmeyer, R. D. and Martínez García, E., Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 333–347, 1990.
Oliveira, J. T., Horn, M., and Paproth, E.: Preliminary note on the stratigraphy of the Baixo Alentejo Flysch Group, Carboniferous of Southern Portugal and on the palaeogeographic development, compared to corresponding units in Northwest Germany, Comunicações dos Serviços Geológicos de Portugal, 65, 151–198, 1979.
Oliveira, J. T., Pereira, Z., Carvalho, P., Pacheco, N., and Korn, D.: Stratigraphy of the tectonically imbricated lithological succession of the Neves Corvo mine area, Iberian Pyrite Belt, Portugal, Miner. Depos., 39, 422–436, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-004-0415-2, 2004.
Pearce, T. H.: A contribution to the theory of variation diagrams, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 19, 142–157, https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00635485, 1968.
Pearce, J. A.: A User's Guide to Basalt Discrimination Diagrams, in: Trace Element Geochemistry of Volcanic Rocks: Applications for Massive Sulphide Exploration, edited by: Wyman, D. A., Short Course Notes, Vol. 12, Geological Association of Canada, 79–113, 1996.
Pereira, Z., Matos, J. X., Fernandes, P., and Oliveira, J. T.: Palynostratigraphy and systematic palynology of the Devonian and Carboniferous sucessions of the South Portuguese Zone, Portugal, Memórias do Instituto Nacional de Engenharia, Tecnologia e Inovação Instituto Nacional de Engenharia, Tecnologia e Inovação, Lisboa, 181 pp., 2008.
Piantone, P., Freyssenet, P., Sobol, F., and Leistel, J.: Distribution of selected major and trace elements in volcanic host of Rio Tinto massive sulfide deposits, in: Current research in geology applied to ore deposits, edited by: Fenoll Hach-Alí, P. F., Torres-Ruiz, J., and Gervilla, F., Proceedings of the 2nd Biennal SGA Meeting, Granada, 9–11 September 1993, 365–368, 1993.
Piantone, P., Freyssenet, P., and Sobol, F.: Geochemical and mineralogical signatures of hydrothermal alteration in the Río Tinto anticline: the massive sulfide deposits of the south Iberian Pyrite Province: geological setting and exploration criteria, in: Substances Minérales et Énergiques, Documents du BRGM 234, edited by: Leistel, J. and Leca, X., Ed. BRGM., 139–161, 1994.
Piercey, S. J., Peter, J. M., Mortensen, J. K., Paradis, S., Murphy, D. C., and Tucker, T. L.: Petrology and U-Pb Geochronology of Footwall Porphyritic Rhyolites from the Wolverine Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposit, Yukon, Canada: Implications for the Genesis of Massive Sulfide Deposits in Continental Margin Environments, Econ. Geol., 103, 5–33, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.103.1.5, 2008.
Quesada, C.: Geological constraints on the Paleozoic tectonic evolution of tectonostratigraphic terranes in the Iberian Massif, Tectonophysics, 185, 225–245, https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(91)90446-Y, 1991.
Quesada, C.: Estructura del sector español de la Faja Pirítica: implicaciones para la exploración de yacimientos, Boletín Geológico y Minero, 107, 65–78, 1996.
Quesada, C.: A reappraisal of the structure of the Spanish segment of the Iberian Pyrite Belt, Miner. Depos., 33, 31–44, 1998.
Relvas, J. M. R. S.: Estudo geológico e metalogenético da área do Gavião, Baixo Alentejo, MsC, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal, 248 pp., 1991.
Relvas, J. R. M. S., Massano, C. M. R., and Barriga, F. J. A. S.: Ore zone hydrothermal alteration around the Gaviäo orebodies: implications for exploration in the Iberian Pyrite Belt, VIII Semana de Geoquimica, Lisboa, 3, 1990.
Relvas, J. M., Tassinari, C. C., Munhá, J., and Barriga, F. J.: Multiple sources for ore-forming fluids in the Neves Corvo VHMS Deposit of the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Portugal): strontium, neodymium and lead isotope evidence, Miner. Depos., 36, 416–427, https://doi.org/10.1007/s001260100168, 2001.
Relvas, J. M. R. S., Barriga, F. J. A. S., Pinto, Á., Ferreira, A., Pacheco, N., Noiva, P., Barriga, G., Baptista, R., de Carvalho, D., Oliveira, V., Munhá, J., Richard, W. H., Goldfarb, R. J., and Nielsen, R. L.: The Neves-Corvo Deposit, Iberian Pyrite Belt, Portugal: Impacts and Future, 25 Years after the Discovery, in: Integrated Methods for Discovery: Global Exploration in the Twenty-First Century, edited by: Goldfarb, R. J. and Nielsen, R. L., Society of Economic Geologists, 9, 155–176, https://doi.org/10.5382/sp.09.08, 2002.
Relvas, J. M. R. S., Barriga, F. J. A. S., Ferreira, A., Noiva, P. C., Pacheco, N., and Barriga, G.: Hydrothermal Alteration and Mineralization in the Neves-Corvo Volcanic-Hosted Massive Sulfide Deposit, Portugal. I. Geology, Mineralogy, and Geochemistry, Econ. Geol., 101, 753–790, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.101.4.753, 2006.
Ribeiro, A. and Silva, J. B.: Structure of South Portuguese Zone, Memórias dos Serviços Geológicos de Portugal, 39, 83–90, 1983.
Rieger, P., Magnall, J. M., Gleeson, S. A., Schleicher, A. M., Bonitz, M., and Lilly, R.: The mineralogical and lithogeochemical footprint of the George Fisher Zn-Pb-Ag massive sulphide deposit in the Proterozoic Urquhart Shale Formation, Queensland, Australia, Chem. Geol., 560, 119975, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119975, 2021.
Rosa, D. R. N., Inverno, C. M. C., Oliveira, V. M. J., and Rosa, C. J. P.: Geochemistry of volcanic rocks, Albernoa Area, Iberian Pyrite Belt, Portugal, Int. Geol. Rev., 46, 366–383, https://doi.org/10.2747/0020-6814.46.4.366, 2004.
Rosa, D. R. N., Inverno, C. M. C., Oliveira, V. M. J., and Rosa, C. J. P.: Geochemistry and geothermometry of volcanic rocks from Serra Branca, Iberian Pyrite Belt, Portugal, Gondwana Res., 10, 328–339, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2006.03.008, 2006.
Ross, P.-S., Bourke, A., and Fresia, B.: Improving lithological discrimination in exploration drill-cores using portable X-ray fluorescence measurements: (2) applications to the Zn-Cu Matagami mining camp, Canada, Geochem-Eplor. Env. A., 14, 187–196, https://doi.org/10.1144/geochem2012-164, 2014.
Ross, P.-S., Bourke, A., Mercier-Langevin, P., Lépine, S., Leclerc, F., and Boulerice, A.: High-Resolution Physical Properties, Geochemistry, and Alteration Mineralogy for the Host Rocks of the Archean Lemoine Auriferous Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposit, Canada, Econ. Geol., 111, 1561–1574, https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.111.7.1561, 2016.
Ross, P.-S., Bourke, A., Schnitzler, N., and Conly, A.: Exploration Vectors from Near Infrared Spectrometry near the McLeod Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposit, Matagami District, Québec, Econ. Geol., 114, 613–638, https://doi.org/10.5382/econgeo.4656, 2019.
Ruiz, C., Arribas, A., and Arribas Jr., A.: Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Masa Valverde blind massive sulphide deposit, Iberian Pyrite Belt (Spain), Ore Geol. Rev., 19, 1–22, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1368(01)00037-3, 2002.
Sáez, R., Pascual, E., Toscano, M., and Almodóvar, G. R.: The Iberian type of volcano-sedimentary massive sulphide deposits, Miner. Depos., 34, 549–570, https://doi.org/10.1007/s001260050220, 1999.
Sáez, R., Moreno, C., González, F., and Almodóvar, G. R.: Black shales and massive sulfide deposits: causal or casual relationships? Insights from Rammelsberg, Tharsis, and Draa Sfar, Miner. Depos., 46, 585–614, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-010-0311-x, 2011.
Sánchez España, J.: Mineralogía y geoquímica de yacimientos de sulfuros masivos en el área nor-oriental de la Faja Pirítica Ibérica (San Telmo – San Miguel – Peña del Hierro), norte de Huelva, España, Doctor of Philosophy, Departamento de Mineralogía y Petrología, Universidad del País Vasco, Leioa, Spain, 2000.
Sánchez-España, J., Velasco, F., and Yusta, I.: Hydrothermal alteration of felsic volcanic rocks associated with massive sulphide deposition in the northern Iberian Pyrite Belt (SW Spain), Appl. Geochem., 15, 1265–1290, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00119-5, 2000.
Sánchez-España, J., Velasco, F., Boyce, A. J., and Fallick, A. E.: Source and evolution of ore-forming hydrothermal fluids in the northern Iberian Pyrite Belt massive sulphide deposits (SW Spain): evidence from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes, Miner. Depos., 38, 519–537, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-002-0326-z, 2003.
Schermerhorn, L. J. G.: An outline stratigraphy of the Iberian Pyrite Belt, Boletín Geológico y Minero, 82, 23–52, 1971.
Schermerhorn, L. J. G.: Spilites, regional metamorphism and subduction in the Iberian Pyrite Belt: some comments, Geologie en Mijnbouw, 54, 23–35, 1975.
Schlatter, D. M.: Volcanic stratigraphy and hydrothermal alteration of the Petiknäs South Zn-Pb-Cu-Au-Ag volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposit, Sweden, PhD, Department of Chemical Engineering and Geosciences, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 2007.
Silva, J. B., Oliveira, J. T., and Ribeiro, A.: Structural Outline, in: Pre-Mesozoic Geology of Iberia, edited by: Dallmeyer, R. D., and Garcia, E. M., Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 348–362, 1990.
Soltani Dehnavi, A., Lentz, D. R., McFarlane, C. R. M., and Walker, J. A.: Quantification of fluid-mobile elements in white mica by LA-ICP-MS: From chemical composition to a potential micro-chemical vectoring tool in VMS exploration, J. Geochem. Explor., 188, 290–307, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.01.017, 2018a.
Soltani Dehnavi, A., McFarlane, C. R. M., Lentz, D. R., and Walker, J. A.: Assessment of pyrite composition by LA-ICP-MS techniques from massive sulfide deposits of the Bathurst Mining Camp, Canada: From textural and chemical evolution to its application as a vectoring tool for the exploration of VMS deposits, Ore Geol. Rev., 92, 656–671, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.10.010, 2018b.
Soltani Dehnavi, A., McFarlane, C. R. M., Lentz, D. R., McClenaghan, S. H., and Walker, J. A.: Chlorite-white mica pairs' composition as a micro-chemical guide to fingerprint massive sulfide deposits of the Bathurst Mining Camp, Canada, Minerals, 9, 125, https://doi.org/10.3390/min9020125, 2019.
Strauss, G. K., Roger, G., Lecolle, M., and Lopera, E.: Geochemical and geologic study of the volcano-sedimentary sulfide orebody of La Zarza, Province of Huelva, Spain, Econ. Geol., 76, 1975–2000, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.76.7.1975, 1981.
Thiéblemont, D., Pascual, E., and Stein, G.: Magmatism in the Iberian Pyrite Belt: petrological constraints on a metallogenic model, Miner. Depos., 33, 98–110, https://doi.org/10.1007/s001260050135, 1997.
Tornos, F.: Environment of formation and styles of volcanogenic massive sulfides: The Iberian Pyrite Belt, Ore Geol. Rev., 28, 259–307, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2004.12.005, 2006.
Tornos, F. and Heinrich, C. A.: Shale basins, sulfur-deficient ore brines and the formation of exhalative base metal deposits, Chem. Geol., 247, 195–207, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.011, 2008.
Tornos, F., González Clavijo, E., and Spiro, B.: The Filon Norte orebody (Tharsis, Iberian Pyrite Belt): a proximal low-temperature shale-hosted massive sulphide in a thin-skinned tectonic belt, Miner. Depos., 33, 150–169, https://doi.org/10.1007/s001260050138, 1998.
Tornos, F., Solomon, M., Conde, C., and Spiro, B. F.: Formation of the Tharsis massive sulfide deposit, Iberian Pyrite Belt: Geological, lithogeochemical, and stable isotope evidence for deposition in a brine pool, Econ. Geol., 103, 185–214, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.103.1.185, 2008.
Tornos, F., Peter, J. M., Allen, R., and Conde, C.: Controls on the siting and style of volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits, Ore Geol. Rev., 68, 142–163, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.01.003, 2015.
Toscano, M., Almodóvar, G. R., Pascual, E., and Sáez, R.: Hydrothermal alteration related to the ”Masa Valverde” massive sulphide deposit, Iberian Pyrite Belt, Spain, in: Current research in geology applied to ore deposits, edited by: Fenoll Hach-Alí, P. F., Torres-Ruiz, J., and Gervilla, F., Proceedings of the 2nd biennal SGA meeting, Granada, 9–11 September 1993, 389–392, 1993.
Toscano, M., Ruiz de Almodóvar, G., and Sáez, R.: Variación composicional de las sericitas de alteración hidrotermal en sulfuros masivos: ”Masa Valverde” (Huelva), Boletín de la Sociedad Española de Mineralogía, 17, 161–162, 1994.
Valenzuela, A., Donaire, T., Pin, C., Toscano, M., Hamilton, M. A., and Pascual, E.: Geochemistry and U–Pb dating of felsic volcanic rocks in the Riotinto–Nerva unit, Iberian Pyrite Belt, Spain: crustal thinning, progressive crustal melting and massive sulphide genesis, J. Geol. Soc., 168, 717–732, https://doi.org/10.1144/0016-76492010-081, 2011.
Velasco-Acebes, J., Tornos, F., Kidane, A. T., Wiedenbeck, M., Velasco, F., and Delgado, A.: Isotope geochemistry tracks the maturation of submarine massive sulfide mounds (Iberian Pyrite Belt), Miner. Depos., 54, 913–934, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-018-0853-x, 2019.
Williams, D., Stanton, R. L., and Rambaud, F.: The Planes–San Antonio pyritic deposit of Rio Tinto, Spain: its nature, environment and genesis, Transactions-Institution of Mining and Metallurgy. Section B: Applied Earth Science, United Kingdom, 84, 73–82, 1975.
Winchester, J. A., and Floyd, P. A.: Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements, Chem. Geol., 20, 325–343, 1977.
Winter, L. S., Tosdal, R. M., Mortensen, J. K., and Franklin, J. M.: Volcanic Stratigraphy and Geochronology of the Cretaceous Lancones Basin, Northwestern Peru: Position and Timing of Giant VMS Deposits, Econ. Geol., 105, 713–742, https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.105.4.713, 2010.